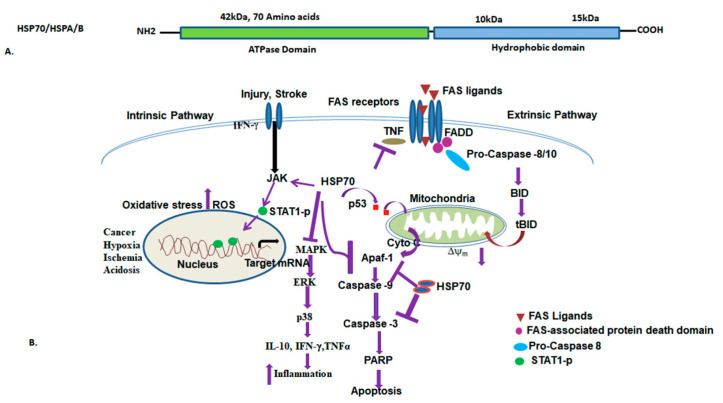
Figure 5.
The diagram depicts the domain arrangement of the HSP70/HSPA/B protein (above) and its associated functions (below). (A) HSP70 comprises two main domains: the ATPase domain and the C-terminal domain. ATP is necessary for activating protein folding by binding to the ATPase domain. (B) HSP70 is implicated in various biological functions. The diagram illustrates its involvement in cellular pathways such as mitochondrial integrity, apoptosis, protein folding, inflammatory responses, and disease regulation. It also represents HSP70’s interactions with other cellular proteins such as p53, TNFα, MAPK, and Apaf-1, which regulate cancer, hypoxia, inflammation, and apoptosis. Loss of the mitochondrial membrane potential leads to apoptotic cell death. Green circle: phosphorylated-STAT1; Marron triangle: FAS-ligands, Violet circle: Fas-associated Protein death domain; Sky-blue oval: Pro-caspase-8; Red box: p53.