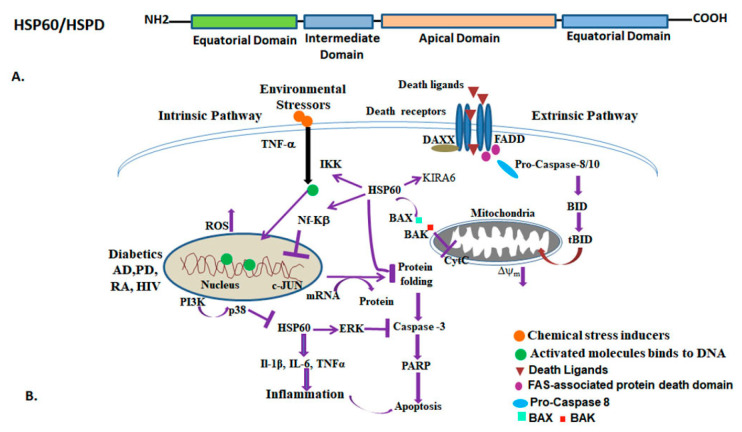
Figure 6.
The diagram depicts the HSP60/HSPD protein domain arrangement (above), and its activation and functions (below). (A) HSP60/GroEL comprises three main domains, the equatorial domain, intermediate domain, and apical domain. (B) The diagram illustrates the involvement of HSP60 in various biological processes. It delineates different cellular pathways such as mitochondrial integrity, apoptosis, protein folding, inflammatory responses, and disease regulation associated with HSP60. HSP60 interacts with other cellular proteins such as BAX, NF-kβ, IKK, and p38 to regulate cancer, diabetes, neurodegeneration, inflammation, and apoptosis. Various stressors and chemical and physical activations of downstream signals regulate protein folding and cell death pathways. Mitochondrial dysfunction and loss of membrane integrity lead to activation of cell death via apoptosis. Abbreviations: Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Human immunodeficiency virus disease (HIV), Rheumatoid arteritis (RA). Red circle: Chemical stress inducers; Green circle: Activated molecules bind to DNA, Marron triangle: Death ligands; Violet circle: Fas-associated Protein death domain; Sky blue oval: Pro-caspase-8; Green box: BAX; Red box: BAK.