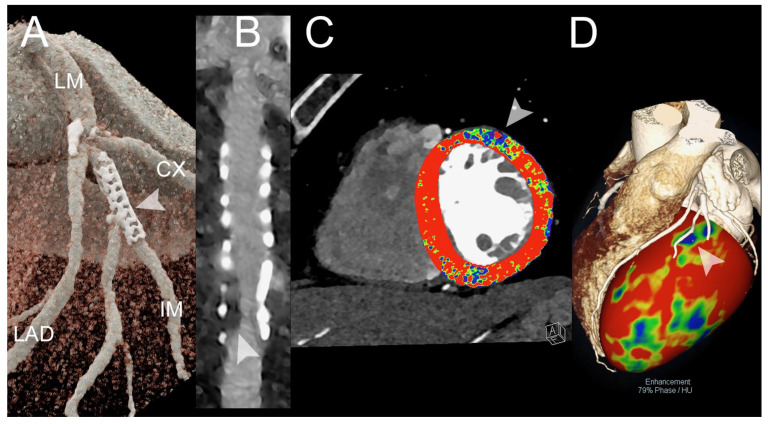
Figure 2.
Spectral cardiac CT angiography of coronary arteries and left ventricle in a patient with previous PCI. The figure shows a spectral CT angiography in a patient with chronic pulmonary embolism displayed with 3D-cinematic rendering (A), a stretched MPR along the central lumen line of the intermediate branch (IM) with a proximal stent (arrowheads in (A)) (B), the first pass rest perfusion image (spectral monochromatic+ 40 KeV with color-coded perfusion overlay) (C), and) the overlay of 3D-volume rendering with the anatomy of the coronary arteries and color-coded perfusion map (D). The figure shows a significant in-stent restenosis (arrowhead in (B)) that causes segmental perfusion delay/defect in rest first-pass perfusion (arrowhead in (C)). The correspondence between the restenosis and the perfusion defect is displayed in (D) (arrowhead). The scan was performed on a commercial whole-body Dual Source Photon-Counting CT scanner (NAEOTOM Alpha, Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany), with 0.2/0.4 mm slice thickness, 0.1/0.2 mm reconstruction increment, FOV 140–160 mm, resolution matrix of 512 × 512/1024 × 1024 pixels on the source axial reconstructions with a kernel filtering of Bv48-60-72 (vascular kernel medium-sharp) and with maximum intensity of Quantum Iterative Reconstruction (QIR 4); the scan is performed with retrospective ECG gating with tube current modulation. The displayed spatial resolution is 0.10/0.20 mm. Abbreviations: PCCT = Photon-Counting CT; PCI = percutaneous coronary intervention; ECG = electrocardiographic.