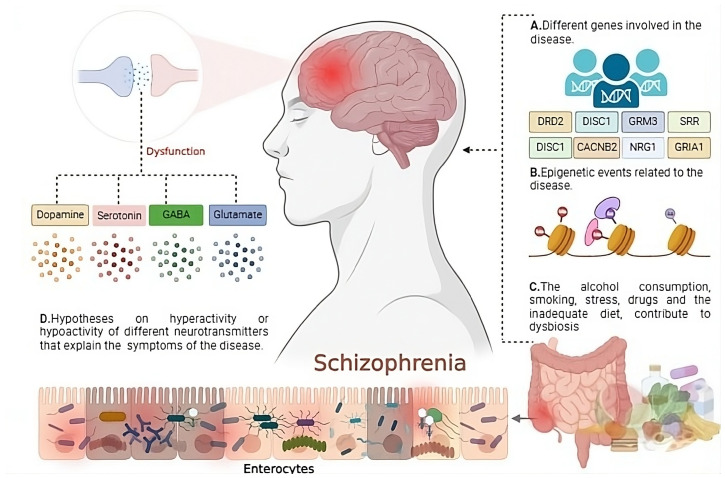
Figure 1.
Diagram of neuroinflammation in schizophrenia. (A) Schizophrenia involves an interplay of genetic predispositions, with genes such as DRD2, DISC1, and GRM3 playing a role in its development. (B) Epigenetic modifications alter gene expression without changing the DNA sequence. (C) Environmental and lifestyle factors, such as alcohol consumption, smoking, stress, drug use, and diet can contribute to intestinal dysbiosis and, consequently, affect the immune and brain systems. (D) Hypotheses on the hyperactivity or hypoactivity of key neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, GABA, and glutamate are considered central to explaining the symptomatology of schizophrenia. The figure was created using BioRender (https://www.biorender.com/) (accessed on 1 January 2024).