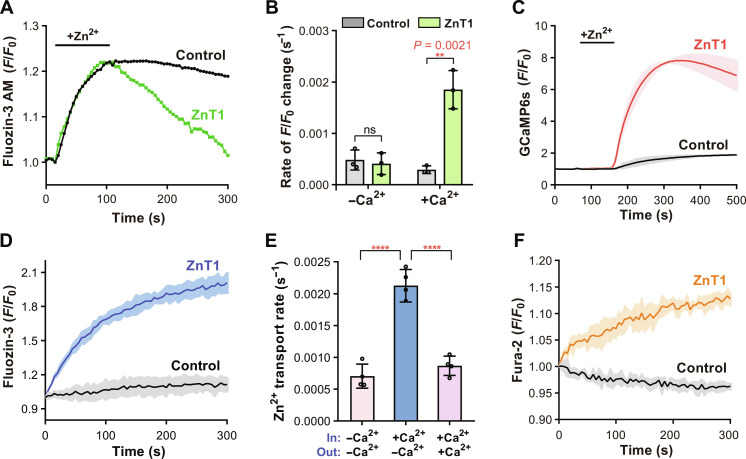
Fig. 1. hZnT1 functions as a Zn2+/Ca2+ exchanger.
(A) Zn2+ efflux by hZnT1 in HEK293T cells. Representative traces of the fluorescence are shown for cells on one coverslip. (B) Initial rates of Zn2+ efflux in HEK293T cells in absence or presence of Ca2+, respectively. Each data point represents the initial rate calculated from the mean of fluorescence changes of at least thirty cells from one coverslip and was repeated three times with three coverslips. (C) Ca2+ influx by hZnT1 in HEK293T cells. Data are obtained with at least thirty cells from one coverslip and repeated three times with three coverslips. (D) Zn2+ efflux by hZnT1 in the proteoliposome-based transport assay. (E) Initial Zn2+ transport rates of hZnT1 determined with the proteoliposomes-based assay. Presence or absence of Ca2+ in assay buffer (out) or inside proteoliposomes (in) is indicated. Data are obtained from four independent experiments. (F) Ca2+ transport by hZnT1 measured in the proteoliposome-based assay. For (C), (D), and (F), fluorescence traces are shown as solid line (mean) with shaded areas (SD) from at least three biological repeats. For (B) and (E), significances were determined using a two-tailed unpaired t test. ns, not significant. ****P < 0.0001. Data are means ± SD.