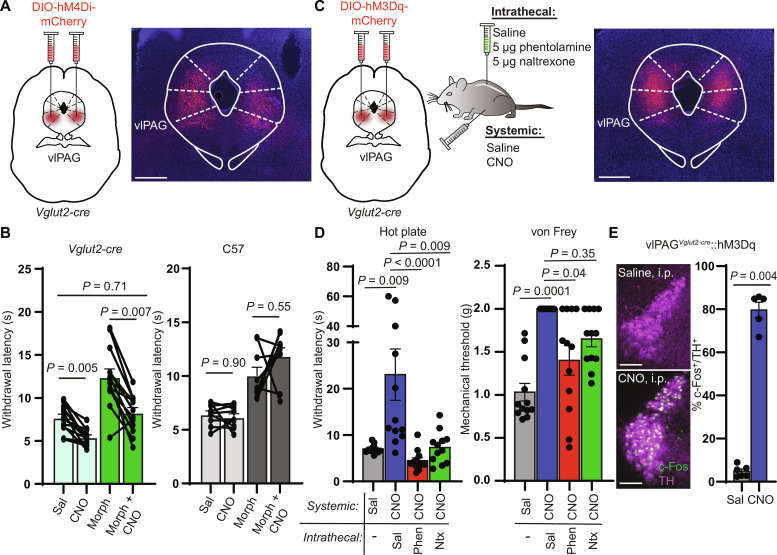
Fig. 3. vlPAG activity is required for systemic morphine antinociception and drives spinal NA–dependent antinociception.
(A) Bilateral vlPAG AAV-DIO-hM4Di-mCherry injections in Vglut2-cre mice with representative image of viral expression. Scale bar, 500 μm. (B) Left: Hot plate withdrawal latencies of vlPAGVglut2-cre::hM4Di mice administered CNO (3 mg/kg i.p.) versus saline without (light green bars) and with morphine (5 mg/kg s.c.) (dark green bars) (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; n = 13 mice; saline versus CNO effect, P < 0.0001, F1,12 = 56.93). Right: Withdrawal latencies of non–virus-injected controls (two-way repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; n = 9 mice; saline versus CNO effect, P = 0.32, F1,8 = 1.143). (C) Bilateral vlPAG AAV-DIO-hM3Dq-mCherry injections in Vglut2-cre mice, combinations of systemic CNO with intrathecal antagonists, and representative image of viral expression. Scale bar, 500 μm. (D) Left: Withdrawal latencies after systemic saline or CNO and intrathecal saline, phentolamine (5 μg), or naltrexone (5 μg) (Friedman test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, n = 12 subjects, P < 0.0001, Friedman statistic = 26.40). Right: Von Frey mechanical thresholds (Friedman test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test, n = 12 subjects, P = 0.0001, Friedman statistic = 21.00). (E) Representative images of c-Fos immunohistochemistry in TH-positive LC neurons of vlPAGVglut2-cre::hM3Dq mice after systemic injection of saline (top) or CNO (bottom). Scale bars, 150 μm. Right: % of TH-positive LC neurons that colocalize with green c-Fos signal (five to eight images analyzed per mouse; n = 6 saline, n = 5 CNO, two-sided Mann-Whitney test). Data in each graph reported as means ± SEM.