Fig. 2 |. Hypothetical model of HIV-mediated myeloid cell and neuronal dysfunction in HIV-associated NCI.
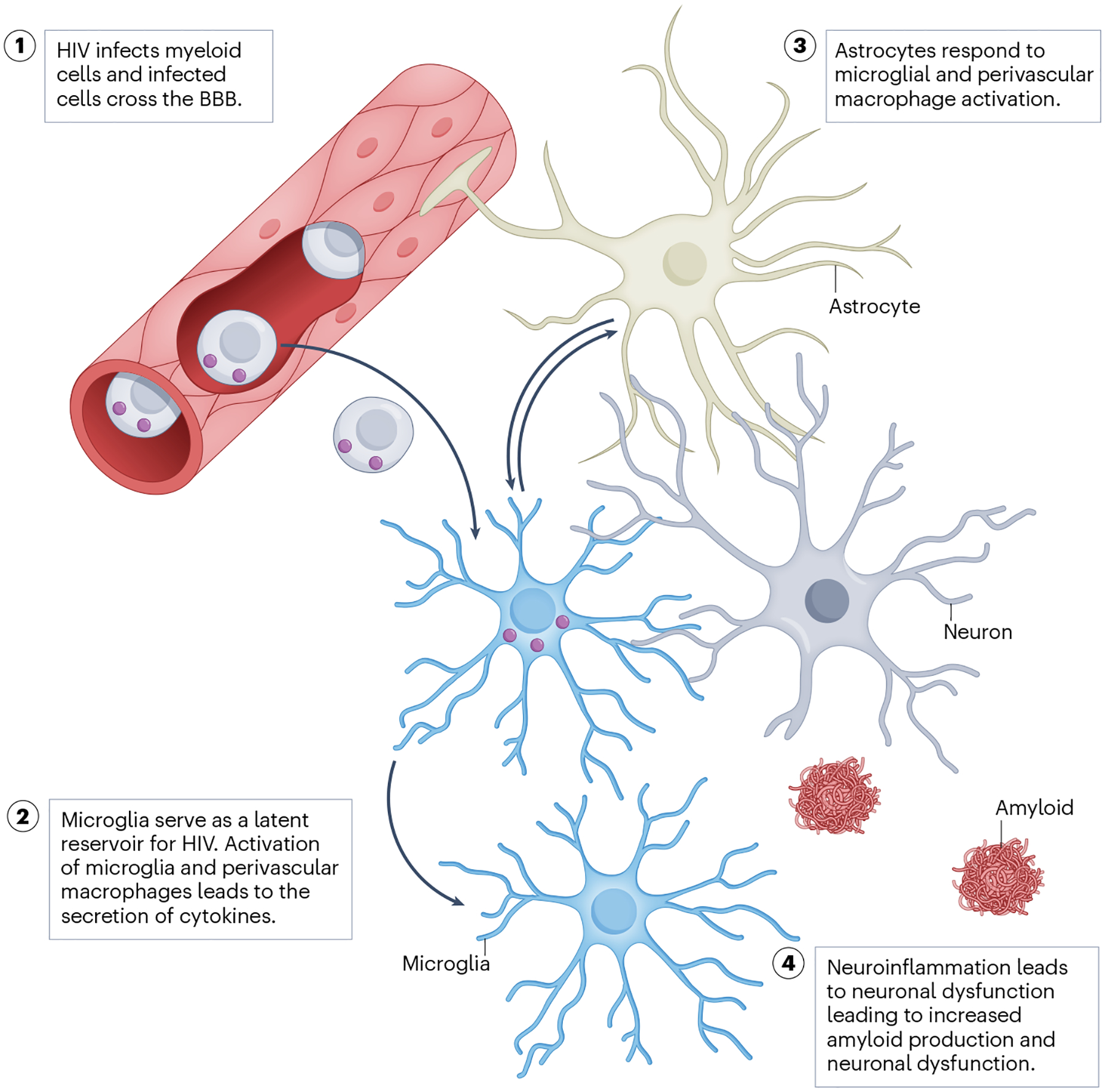
HIV-infected monocytes transmigrate from the peripheral blood to the brain. HIV-infected perivascular macrophages and microglia respond by releasing cytokines that further activate microglia and astrocytes. This eventually leads to neuronal dysfunction, as evidenced by impairment of synaptic transmission, disturbed mitochondrial bioenergetics and, eventually, neurocognitive impairment (NCI). BBB, blood–brain barrier.
