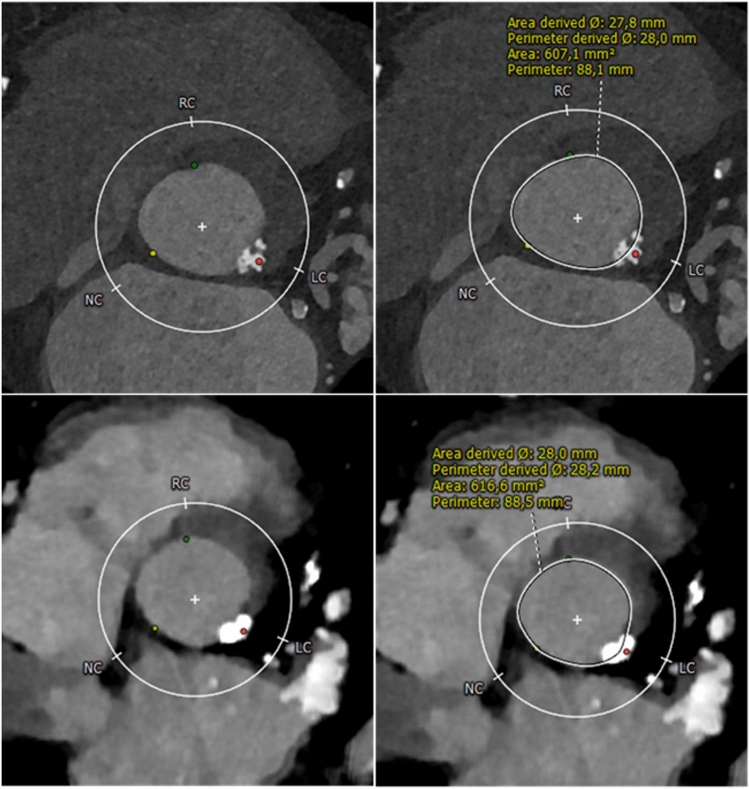
Fig. 2.
Photon-Counting detector CT angiography (CTA) of an 86-year-old male with severe aortic valve stenosis, conducted as a planning for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). The aortic annulus was assessed with ECG-gated retrospective Ultrahigh-Resolution (UHR)-CTA (A, B) and ECG-triggered prospective high-pitch spectral aortoiliac (HPS)-CTA (C, D). Note the superior image quality of UHR-CTA and detailed visualization of the calcified plaque at the aortic annulus. Regardless, pre-TAVR CT measurements were consistent across both methods, with area-derived and perimeter-derived diameters resulting in the same hypothetical prosthesis choice. Notably, the radiation dose was higher for UHR-CTA (651 mGy*cm) than HP-CTA (297 mGy*cm). Note: In panel C and D of HPS-CTA, the area of increased attenuation within the left atrial appendage (arrowhead) represents increased attenuation due to accumulated contrast media