Fig. 3.
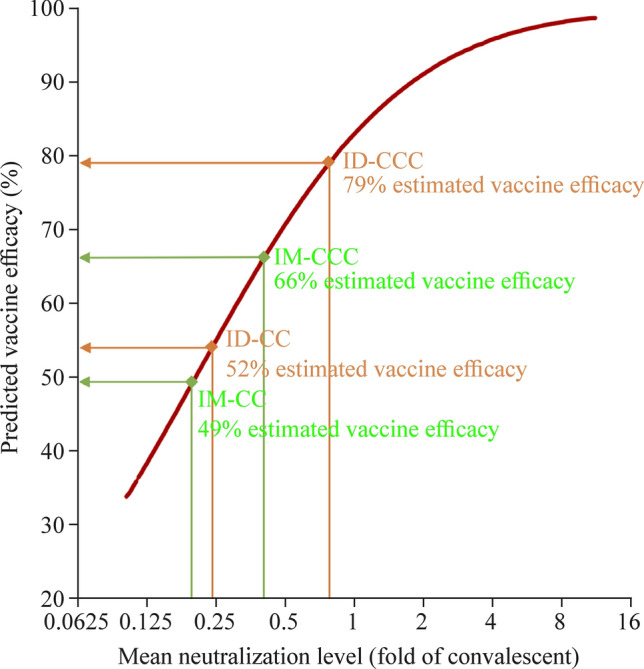
Estimation of vaccine efficacies for 2 doses and 3 doses of CoronaVac by intramuscular or intradermal administration vaccination in the evaluable analysis population based on neutralisation titers against SARS-CoV-2. The vaccine efficacy estimates were based on neutralising antibody titers (PRNT50, or plaque reduction neutralisation test based on the reciprocal of the highest serum dilution that resulted in the cutoff of > 50%) post-dose 2 or post-dose 3 of CoronaVac administered intramuscularly (IM-CC or IM-CCC) or intradermally (ID-CC or ID-CCC), as neutralising antibodies have been established as a reliable correlate of protection that can predict vaccine efficacies against symptomatic COVID-19. Dividing the geometric mean titers of PRNT50 who received vaccination by titers from 102 convalescent sera collected on days 28–59 post-onset of illness in patients aged ≥ 18 years yielded the mean neutralising levels (fold of convalescent). Extrapolation of the point estimates of the vaccine efficacies from the best fit of the logistic model was performed as previously described [14, 15, 40]. IM-CC (n = 119) and IM-CCC (n = 60), post-dose 2 and post-dose 3 of vaccine administered intramuscularly, respectively; ID-CC (n = 54) and ID-CCC (n = 42), post-dose 2 and post-dose 3 of vaccine administered intradermally, respectively. SARS-CoV-2 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019, PRNT plaque reduction neutralisation titre, ID intradermal, IM intramuscular
