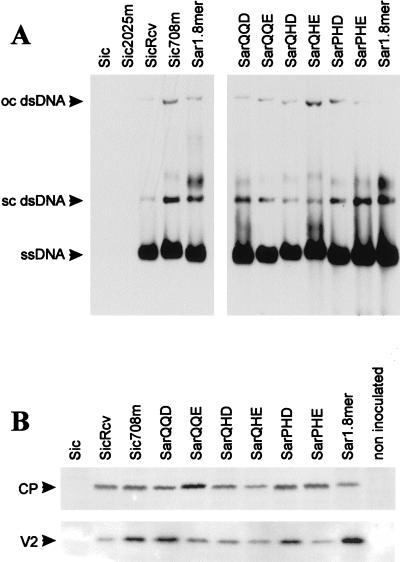
FIG. 2.
Infectivity of TYLCV-Sic and -Sar clones in tomato plants. (A) Analysis of viral DNA. Total DNA extracted with TLES buffer from plants, 4 to 5 weeks after agroinoculation with the wild-type Sic and Sar and with the mutant clones was separated in 1% agarose gels containing ethidium bromide in 0.5× TBE buffer and blotted onto nylon membrane. Viral DNA was detected in Southern blots with a digoxigenin-labelled random-primed DNA probe synthesized on the full-length TYLCV-Sar wild-type genome. Hybridization was performed at 68°C in Standard hybridization buffer (Boehringer Mannheim). Blots were developed with CDP-Star (Tropix), after incubation with goat antidigoxigenin antibody. ssDNA and the replicative supercoiled (sc) or open-circular (oc) dsDNA forms are indicated. (B) Accumulation of CP and V2 protein. Approximately equal amounts of total proteins extracted with TCA from plants agroinoculated with the TYLCV clones were separated in SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (18% polyacrylamide for CP and 20% polyacrylamide for V2). Gels were blotted onto PVDF membranes. For Western blots, an anti-TYLCV-Sar serum (for CP) or an anti-GST-V2 serum (for V2) was used (1/10,000 final dilution). Both sera were previously cross-adsorbed with total proteins from healthy plants. Blots were developed either with an anti-rabbit AP-conjugated antibody and NBT-BCIP for CP or with an anti-rabbit HRP-conjugated antibody and a chemiluminescent substrate for V2. The positions of CP (29 kDa) and V2 (14 kDa) are indicated.