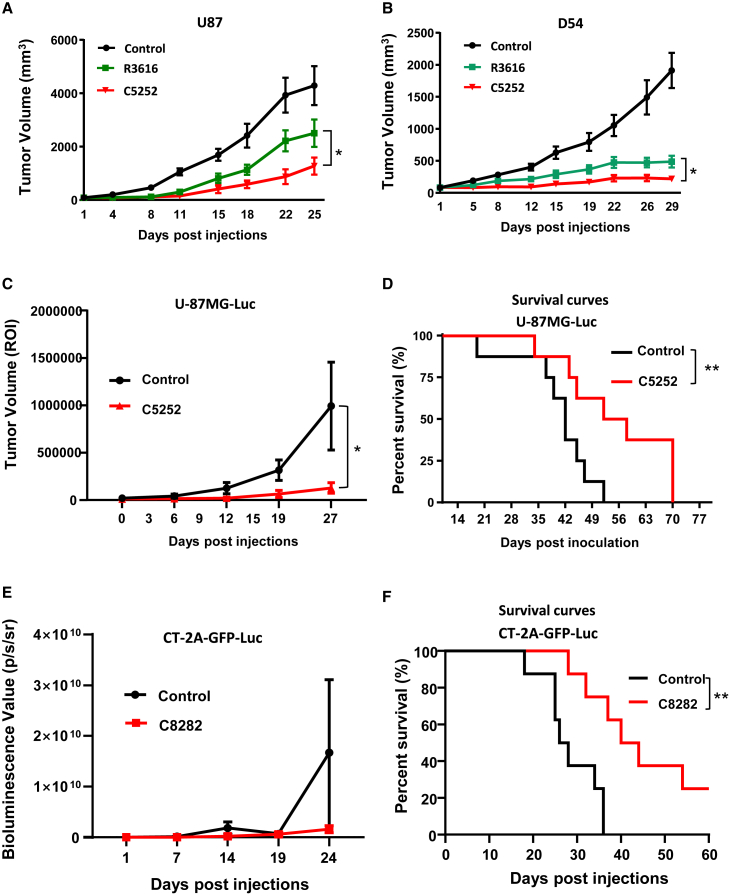
Figure 5.
The anti-tumor therapeutic efficacy of C5252 in a subcutaneous glioblastoma model and an orthotopic glioblastoma model
(A and B) Subcutaneous glioblastoma model. Subcutaneous U87 (A) and D54 (B) tumors were established in BALB/c-derived nude mice. Tumor-bearing mice were treated with intratumoral injections of control, R3616 (5 × 106 PFUs/animal), or C5252 (5 × 106 PFUs/animal) on specified days. Tumor volumes are represented as mean ± SD for 6 animals per group. Statistically significant differences between C5252 and R3616 group are indicated (∗p < 0.05). (C) C5252 in orthotopic tumor model. Female BALB/c nude mice received intracerebral inoculation with U-87MG-Luc tumor cells. Mice were treated with intratumoral injections of C5252 (3 × 105 PFUs/animal in 5 μL) at specific intervals. Tumor volume (ROI) is shown as mean ± SD. Statistically significant differences between C5252 and control group are indicated (∗p < 0.05). The Luc images are presented in Figure S5A. (D) Survival curves. Survival curves demonstrating the significant survival benefit of C5252 treatment are shown. Statistically significant differences between C5252 and control group are indicated (∗∗p < 0.01) using Kaplan-Meier analysis. (E) C8282 in orthotopic tumor model. Female C57BL/6 mice received intracerebral inoculation with CT-2A-GFP-Luc tumor cells (2 × 103 cells/animal). Mice were treated with intratumoral injections of C8282 (1 × 105 PFUs/animal in 5 μL) at specific intervals. Tumor volume (ROI) is shown as mean ± SD. The images are presented in Figure S5B. (F) Survival curves. Survival curves demonstrating the significant survival benefit of C8282 treatment are shown. Statistically significant differences between C8282 and control group are indicated (∗∗p < 0.01) using Kaplan-Meier analysis.