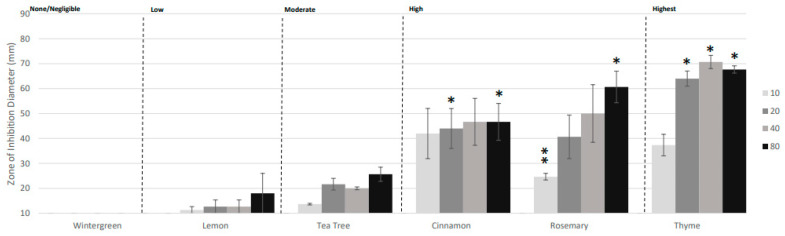
Figure 1.
Volatile antibacterial activity of essential oils against Streptococcus pyogenes. Bacterial zone of inhibition assays were performed measuring the activity of volatile constituents from Gaultheria fragrantissima (Wintergreen), Citrus limon (Lemon), Melaleuca alternifolia (Tea Tree), Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Cinnamon), Rosmarinus officinalis (Rosemary), and Thymus vulgaris (Thyme) essential oils. The results are displayed with a color gradient from light to dark grey to represent the increasing essential oil concentrations, in the order of 0 μL, 10 μL, 20 μL, 40 μL, and 80 μL, respectively. The antimicrobial efficacy was assessed based on the zone of inhibition diameter and categorized as none (<10 mm), negligible (10–15 mm), low (15–30 mm), moderate (30–50 mm), high (50–70 mm), and highest (>70 mm). Error bars denote the standard deviation derived from three separate experiments. Statistically significant deviation of the various essential oils relative to an EtOH control are indicated with asterisks: * p = 0.01–0.05; ** p = 0.001–0.01.