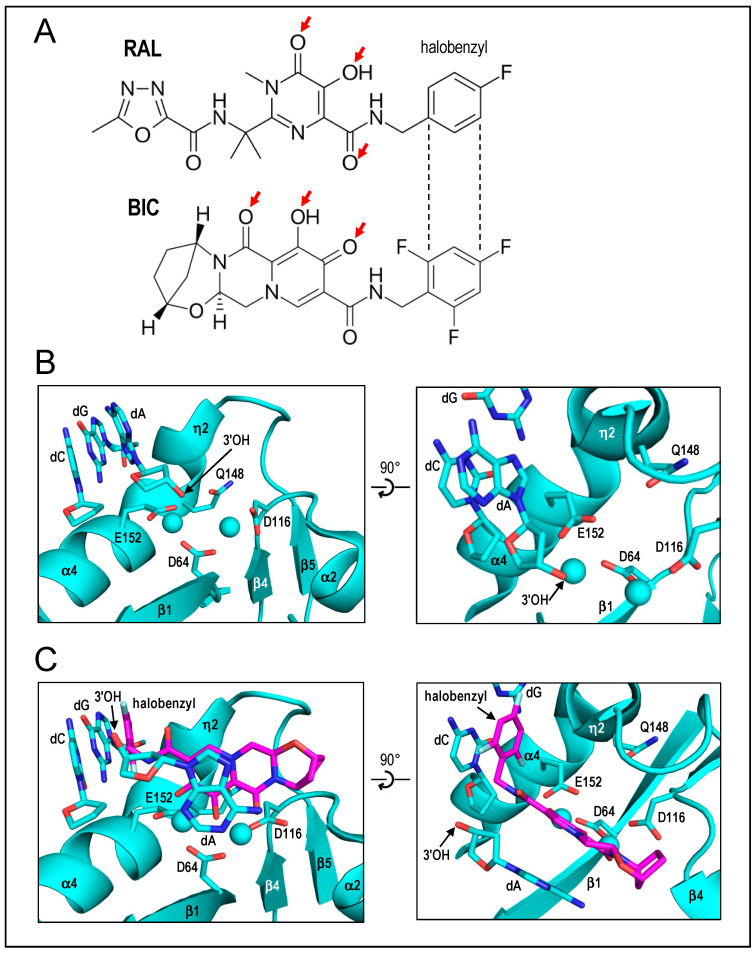
Figure 4.
INSTI and intasome structures. (A) Structures of representative INSTIs RAL and BIC highlighting conserved heteroatoms (red arrows) and halo-benzyl sidechains. (B) Cryo-EM structure of the HIV-1 intasome [Protein Databank (PDB) accession code 6PUT] highlighting DDE catalytic triad residues (D64, D116, E152), CA end of the cleaved viral DNA strand, as well as opposing C-paring dG nucleotide. IN secondary structural elements are labelled. Q148, which can confer significant INSTI resistance when altered, is also highlighted. Spheres, calcium atoms; red and blue, oxygen and nitrogen atoms, respectively. The rightward panel affords an ~90° rotated “top view” of the leftward panel. (C) Same as in panel (B), except with BIC (magenta backbone with grey fluorines) bound (PDB code 6PUW), which displaces dA along with its 3′-OH required for IN strand transfer activity from committed positions at the IN active site. Spheres, Mg2+ ions. Panels (B,C) based on ref. [90].