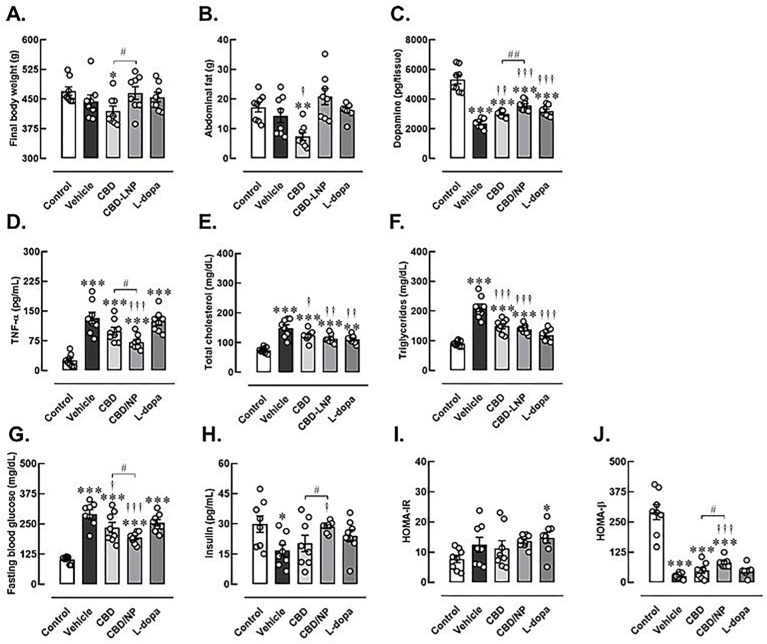
Figure 3.
Changes of physical and biochemical profiles after 4 weeks of vehicle, CBD, CBD lipid nanoparticles (CBD-LNP), or levodopa (L-dopa) treatments in diabetic Parkinson’s disease (DP) rats as determined by neuroinflammatory and metabolic biomarkers. (A) Final body weight, (B) abdominal fat weight, (C) striatal dopamine, (D) proinflammatory TNF-α, (E) total cholesterols, (F) triglycerides, (G) fasting blood glucose, (H) insulin, (I) HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment for insulin resistance), and (J) HOMA-β (Homeostatic Model Assessment estimates steady state beta cell function). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 8 rats/group). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 compared to control, † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01, ††† p < 0.001 compared to vehicle treated-DP group and # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 compared to CDB treated-DP group.