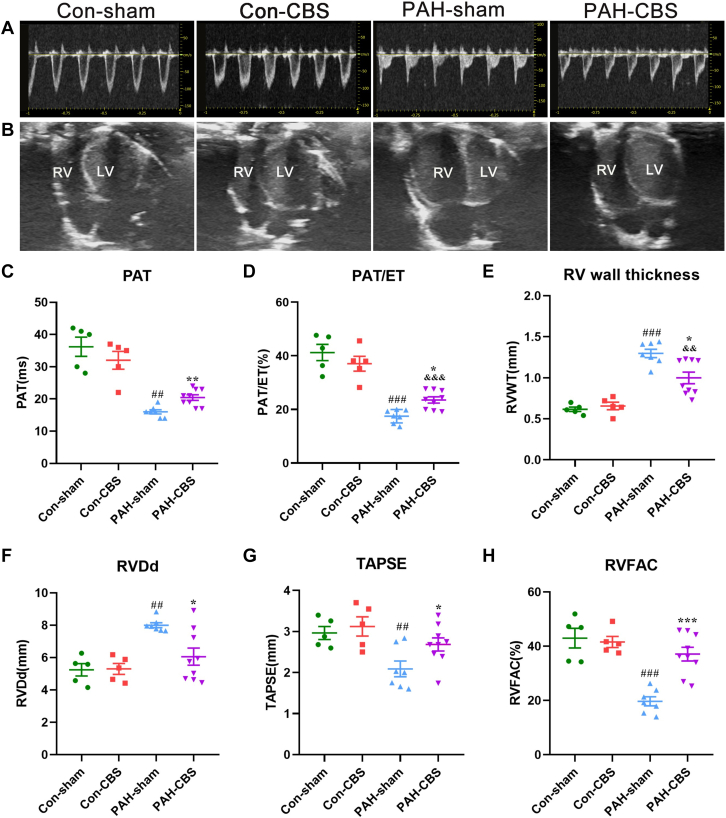
Figure 4.
Effects of CBS on Pulmonary Flow and RV Function in MCT-Induced PAH Rats
Representative images of pulmonary blood flow (A) and apical 4-chamber view (B) at the fourth week after MCT injection. CBS increased pulmonary acceleration time (PAT) (C) and PAT/ejection time (ET) ratio (D) in PAH rats. CBS decreased RV wall thickness (RVWT) (E) and RV dimension in diastole (RVDd) (F) in PAH rats. CBS increased tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) (G) and RV fractional area change (RVFAC) (H) in PAH rats. Con-sham group, n = 5; con-CBS group, n = 5; PAH-sham group, n = 7; PAH-CBS group, n = 9. Values are mean ± SEM. ##P < 0.01 vs con-sham and ###P < 0.001 vs con-sham; ∗P < 0.05 vs PAH-sham, ∗∗P < 0.01 vs PAH-sham, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs PAH-sham; &&P < 0.01 vs con-CBS and &&&P < 0.001 vs con-CBS by 1-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey or Tamhane T2 post hoc test. LV = left ventricle; other abbreviations as in Figures 1 and 3.