Figure 1.
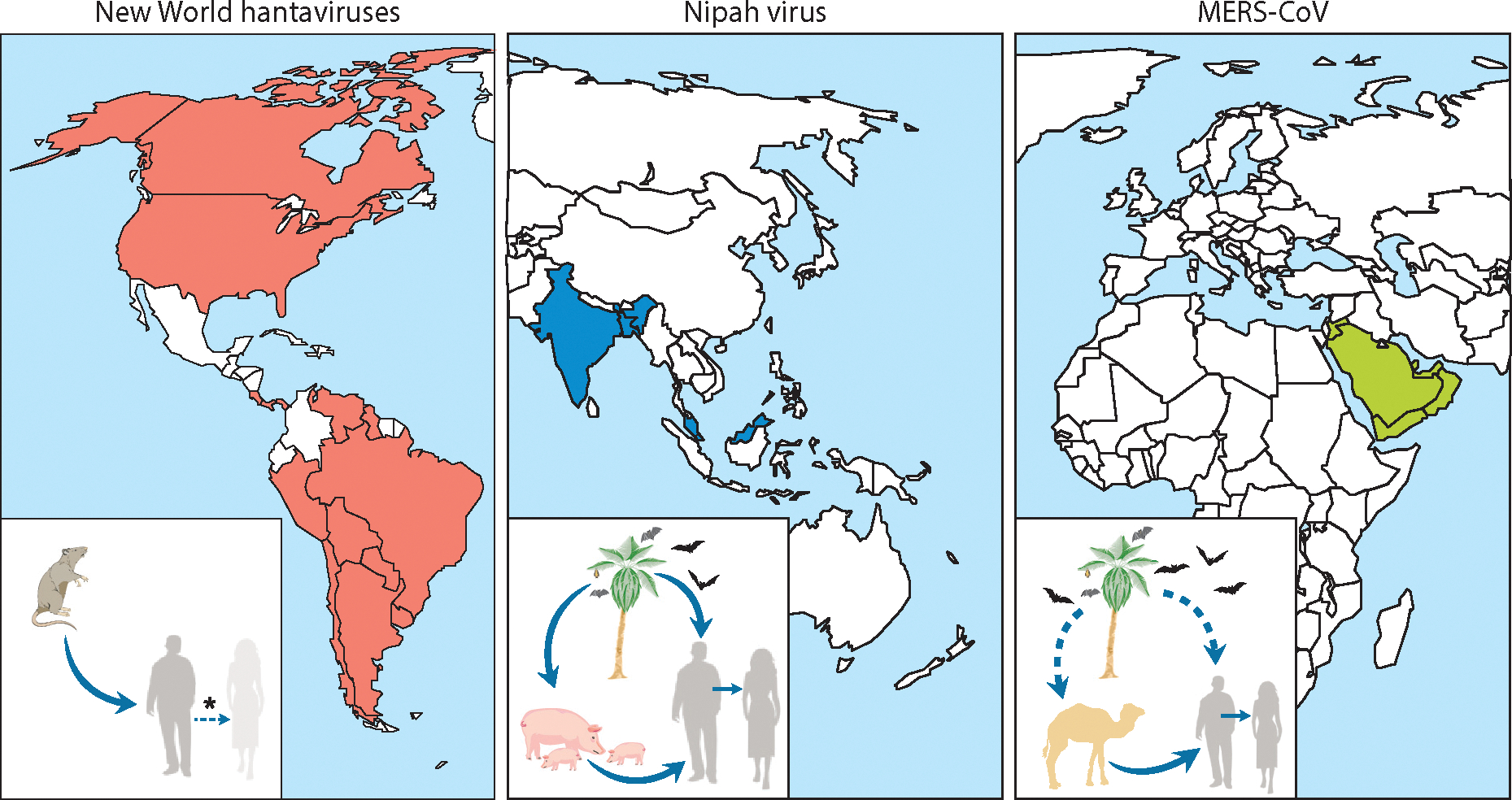
The geographic spread and zoonotic transmission of New World hantaviruses, Nipah virus, and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Endemic regions where human cases have been identified are indicated on the map for each virus. Insets display the zoonotic transmission cycle of each virus. New World hantaviruses are transmitted directly from their rodent reservoir to humans; human-to-human transmission has occurred on rare occasion, but only for Andes virus (asterisk). Nipah virus is transmitted from its fruit bat reservoir directly or via an intermediate/amplifying host, the pig. Subsequent human-to-human transmission occurs regularly in Bangladesh. The transmission cycle of MERS-CoV is currently not completely resolved because the natural reservoir has not been definitively established. MERS-CoV is either transmitted directly from its reservoir in bats or dromedary camels, or is transmitted via dromedary camels as an intermediate/amplifying host; subsequent human-to-human and/or nosocomial transmission occurs regularly.
