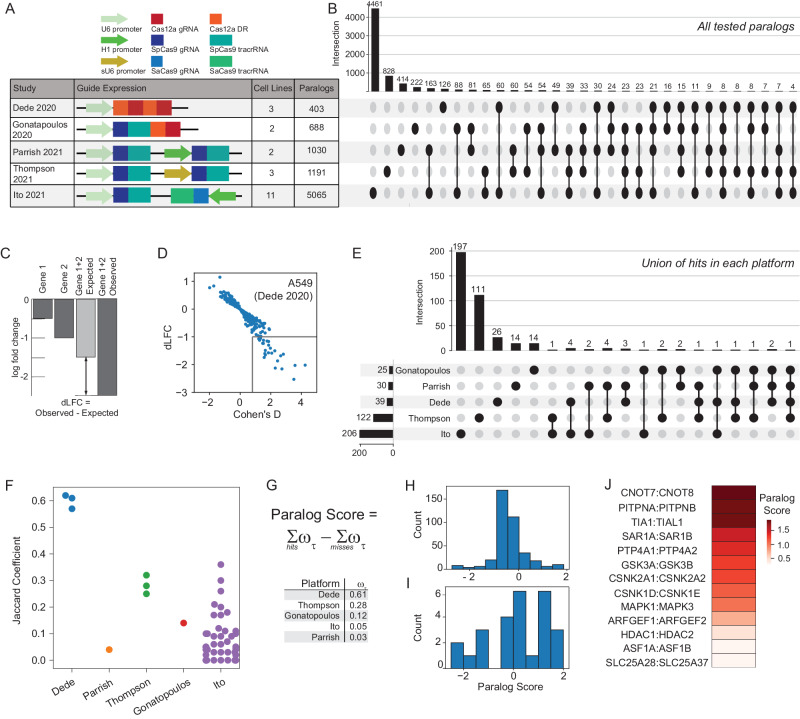
Fig. 1. Comparative analysis of paralog synthetic lethality screens.
A Different multiplex CRISPR perturbation methods applied to assay paralog synthetic lethality. B Tested paralog pairs in each study. Upset plot shows the intersection of pairs across different studies. C Quantifying synthetic lethality between paralog pairs. Single mutant fitness (SMF) is the mean log fold change of gRNAs that target an individual gene. Expected double mutant fitness (DMF) is calculated as the sum of SMF of gene 1 and gene 2. Delta Log Fold Change (dLFC) is the difference between observed and expected fold change and is used as a measure of genetic interaction. D dLFC vs. Cohen’s D in one data set, A549 screen in Dede. E Comparison of union of hits across all cell lines in each study. F Jaccard coefficient comparing hits across all pairs of cell lines within each study. G The “paralog score” is the weighted sum of hits minus the weighted sum of misses; i.e. where the gene pair is assayed but not a hit. Weights are the median of the platform-level Jaccard coefficients from F. H Histogram of paralog scores of 388 hits across all 5 studies. I Histogram of paralog scores across 26 hits in >1 study. J Thirteen candidate “paralog gold standards” with paralog score >0.25 and hit in more than one study. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.