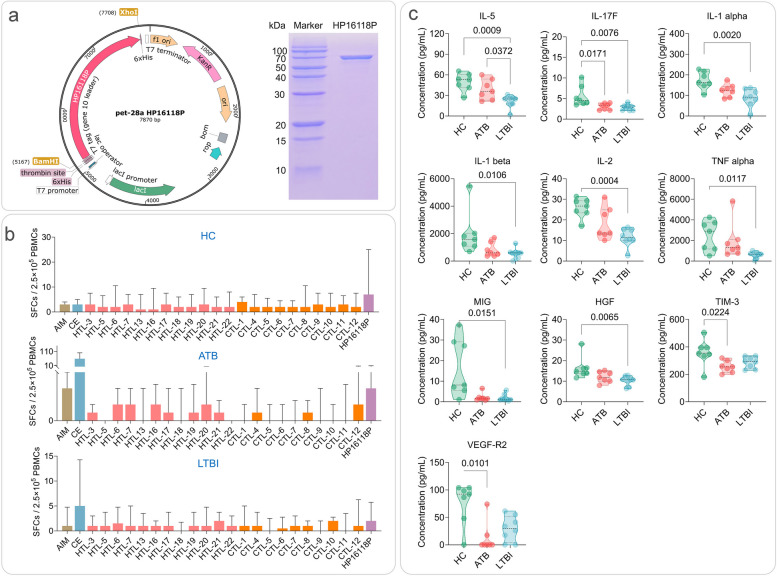
Fig. 3.
Construction and expression of HP16118P and the number of IFN-γ+ T lymphocytes and cytokines induced by HP16118P in HC, ATB, and LTBI groups. a Schematic diagram of the recombinant plasmid of HP16118P and protein purification gel electrophoresis. b Detection of IFN-γ+ T lymphocytes by enzyme-linked immunospot assay (ELISPOT) after HP16118P stimulation of PBMCs. HP16118P, 12 HTL epitope peptides, 10 CTL epitope peptides, AIM medium (negative control), and CE (positive control) were used to stimulate PBMCs from healthy individuals (n = 23), ATB patients (n = 19), and LTBI individuals (n = 24). The frequency of IFN-γ+ T lymphocytes was detected using the ELISPOT method. c Differential cytokine induction by HP16118P in HC, ATB, and LTBI groups. PBMCs from HCs (n=7), ATB (n=8), and LTBI (n=7) individuals were stimulated with HP16118P in vitro, and the culture supernatant was collected after 48 hours for high-throughput liquid chromatography protein analysis to detect the expression levels of 35 cytokines. Results showed significant differences in cytokines, including IL-5, IL-17F, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-2, TNF-α, MIG, HGF, TIM-3, VEGF-R2, among the three groups. The data were analyzed using the non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis test, with a significance level of P < 0.05. The data are presented as medians and interquartile ranges. AIM, auto-induction medium; SFCs, spot-forming cells; HTL, helper T lymphocytes; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; CE, the fusion protein of CFP-10 and ESAT-6; ATB, active tuberculosis; LTBI, latent tuberculosis infection; PBMC, peripheral blood mononuclear cells