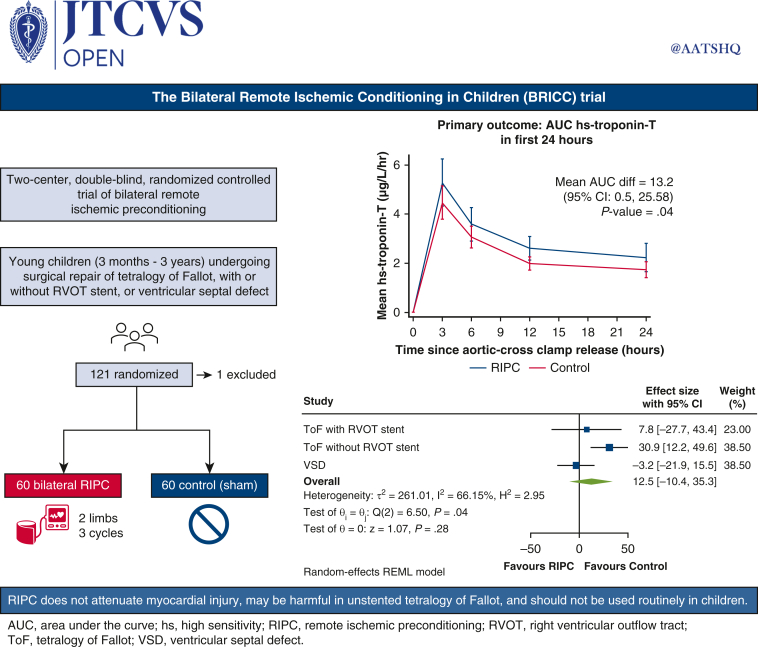
Figure 1.
The Bilateral Remote Ischemic Conditioning in Children trial. A 2-center, double-blind, randomized controlled trial in which 120 young children with the 2 most common congenital heart defects requiring surgery were randomized to bilateral RIPC or sham intervention. AUC for hs-troponin-T in the first 24 hours was higher in the preconditioning group than in controls (P = .04), and subgroup analysis suggested a differential effect by underlying defect (pinteraction = .04). Bilateral RIPC does not attenuate myocardial injury during surgery in young children, with evidence of potential harm in unstented TOF, and its routine use cannot be recommended. AUC, Area under the curve; CI, confidence interval; RVOT, right ventricular outflow tract; RIPC, remote ischemic preconditioning; ToF, tetralogy of Fallot; VSD, ventricular septal defect; hs, high sensitivity.