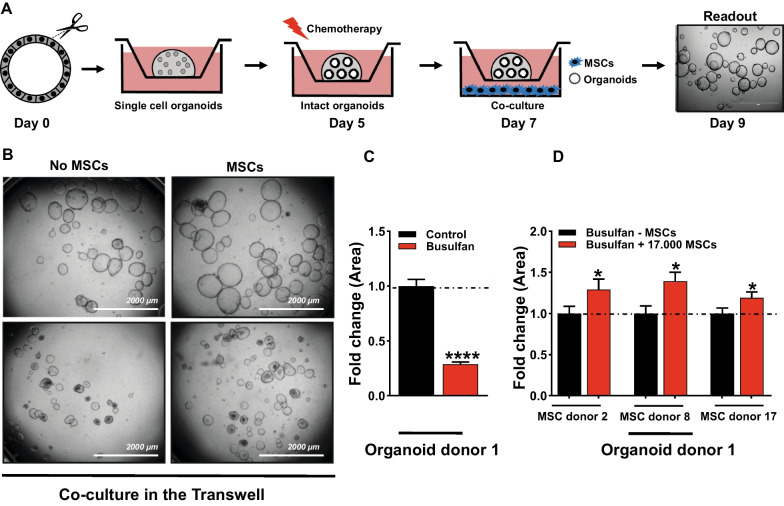
Fig. 3.
MSC secretome contributes to the rescue of busulfan-induced damage of small intestine organoids. A Schematic overview of the in vitro co-culture model of MSCs and small intestine organoids damaged by treatment with busulfan in a Transwell insert system. Single cell small intestine organoids were embedded in matrigel, grown for 5 days (day 0–5) in the Transwell insert, and treated with busulfan for 48 h (day 5–7). Organoids damaged by busulfan were co-cultured with 17,000 MSCs grown in the lower compartment of the Transwell system for 48 h (day 7–9) and the surface area of organoids were assessed at day 9. B Representative images of control organoids and organoids treated with busulfan co-cultured in Transwell system without or with 17,000 MSCs at 48 h after co-culture are shown. C Busulfan reduced the size of the donor 1 organoids. D Co-culture with MSCs in the Transwell system increased the size of the donor 1 organoids. The quantification of surface area of the organoids was represented as fold change as compared to control. Results are shown as means ± SEM of data from organoid donor 1. Due to the large biological variation in organoid size, the statistical analysis of the effect of individual MSC donors on the size of busulfan-induced damaged organoids was based on all evaluable individual organoids (1 organoid/matrigel droplet cultured in different wells in duplicate). Scale bars, 2000 µm. * p < 0.05, and **** p < 0.0001 as compared to control (Kruskal–Wallis test or a Mann Whitney test or one-way ANOVA)