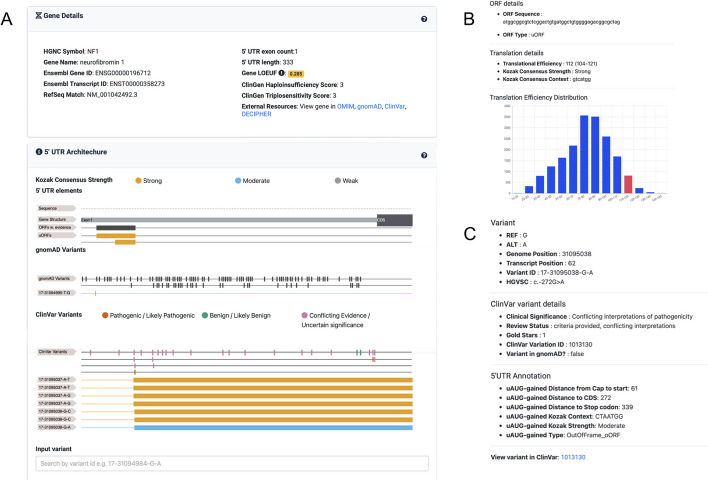
Fig. 4.
VuTR: an interactive web-based tool. A A screenshot from VuTR showing the NF1 gene. The top section displays summary gene details and links to other tools and databases. The following section, titled ‘5’UTR Architecture’, shows the gene’s native 5’UTR exon structure, predicted uAUG elements, and Ribo-Seq uORFs. NF1 features two predicted uORFs, both with a strong Kozak consensus strength (shown by the yellow colour), the longer 45 bp uORF is also found in the Ribo-Seq dataset. Variants observed in gnomAD and ClinVar are displayed in separate tracks. Each variant that creates a uORF or disrupts a predicted uORF is shown on a separate row. Here, a variant that disrupts the start of the longer predicted uORF, which is also found in the Ribo-Seq data (uAUG-lost; 17-31094995-T-G) is observed in gnomAD. Four ClinVar variants create out-of-frame ORFs (oORFs) by either disrupting the stop codon of the two native uORFs (uSTOP-lost; 17-31095037-A-T, 17-31095037-A-G, 17-31095038-G-C) or by creating a new oORF through a uAUG-gained variant (17-31095038-G-A). B An example of a popup that appears when a uORF / oORF is selected, giving context specific details regarding its sequence, Kozak consensus strength, and a histogram of how its predicted translational efficiency [(6)] compares to all other uORFs / oORFs within MANE 5’ UTR sequences. C An example of a popup that appears when a ClinVar variant is selected. This example shows the uAUG-creating variant, 17-31095038-G-A. The popup displays the variant details, information from ClinVar, and the variant annotation from UTRannotator [38]. uORF: upstream open reading frame