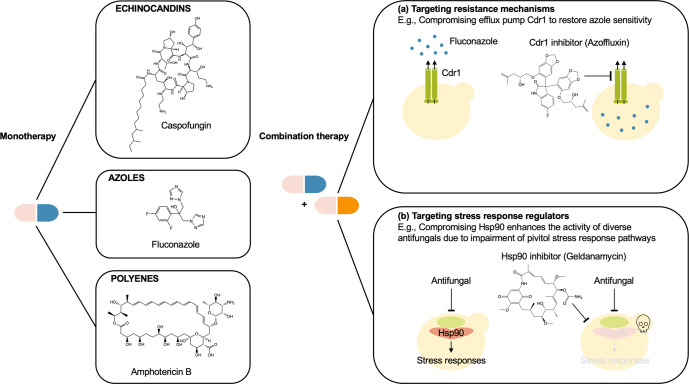
Fig. 3. Combinatorial strategies to combat invasive fungal infections.
Compared with monotherapy, treatment with drug combinations can improve drug efficacy and overcome resistance. a Targeting resistance mechanisms to improve antifungal efficacy due to increased bioavailability against multidrug-resistant pathogens. For example, pharmacological inhibition of efflux pump Cdr1 with a bis-benzodioxolylindolinone (azoffluxin) increases intracellular fluconazole levels, improving fluconazole activity against the emerging pathogen C. auris. b Targeting stress response regulators to enhance antifungal efficacy and impede the emergence of drug resistance. For example, pharmacological inhibition of Hsp90 with geldanamycin abrogates stress responses required to survive antifungal-induced stress.