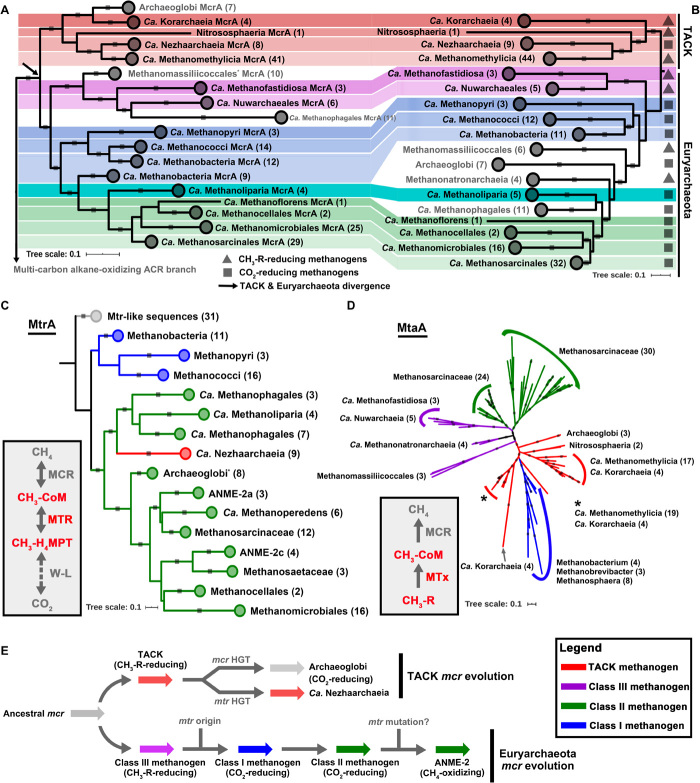
Fig. 1. Phylogenetic analyses of enzymes in archaeal methane metabolism.
(A) The McrA/AcrA phylogenetic tree is constructed on the basis of the alignments of 259 McrA/AcrA sequences with 472 aligned positions. Only the McrA branches are showed here. (B) Phylogenomic affiliation of 177 MAGs is based on 37 conserved protein sequences using representative methane metabolism archaea. Background colors: TACK, red shaded; class I methanogen, blue shaded; class II methanogen, green shaded; class III methanogen, pink shaded. (C) MtrA phylogenetic tree shows the classification of these sequences from different archaeal lineages. The phylogenetic tree is constructed on the basis of the alignments of 152 MtrA sequences with 148 aligned positions. Other phylogenetic trees are presented in fig. S5, which are in agreement with Liu et al. (73). The MtrA and H-like subunits are possibly either HGT from methanogens or originated before class I methanogens, as also described in Wang et al. (74). (D) One type of methyltransferase (MtaA, alpha subunit of methanol-corrinoid protein:coenzyme M methyltransferase) phylogenetic tree (134 sequences with 309 aligned positions) shows that methyltransferases are likely vertically transferred and might originate before the divergence of TACK and Euryarchaeota. Some class I methanogens that contain MtaA might be HGT from the TACK methanogens. Other methyltransferase phylogenetic trees are displayed in fig. S7. All conserved protein phylogenomic and McrA, MtrA, and MtaA phylogenetic alignments are based on MAFFT and then filtered with trimAl, and the trees that were built by the IQ-Tree method with model LG+C60+F+G using SH approximate likelihood ratio test implemented with 1000 bootstrap replicates with bootstrap higher than 0.8 are shown with gray squares on tree branches. (E) Evolutionary history of MCR-based methane metabolism.