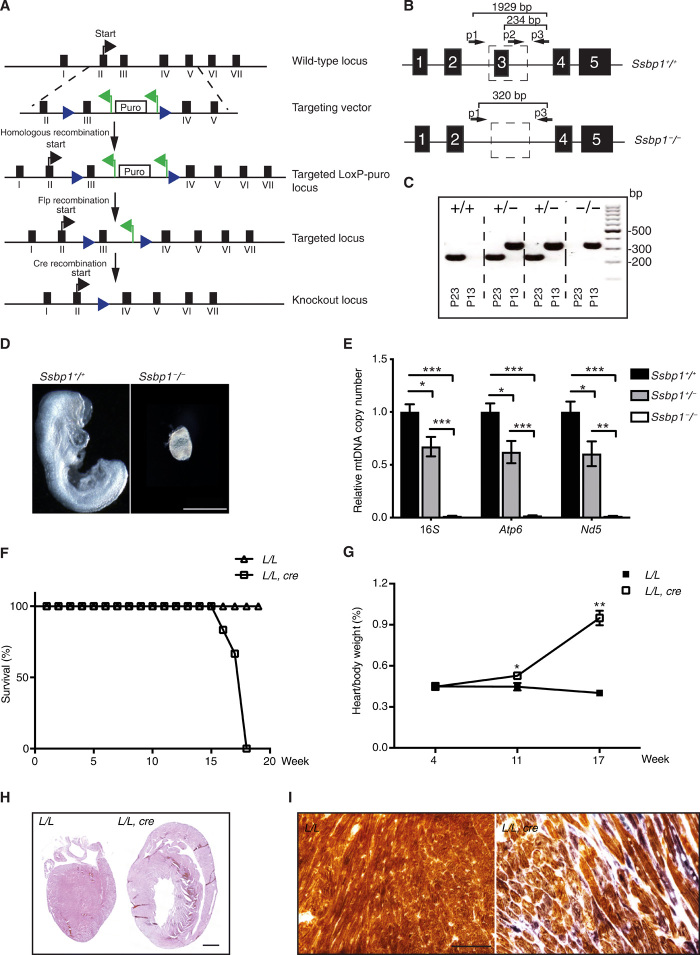
Fig. 1. Germline Ssbp1 knockout leads to embryonic lethality, whereas knockout in the heart and skeletal muscle leads to cardiomyopathy.
(A) Targeting strategy for disruption of the Ssbp1 gene. Blue arrowhead, loxp sequence; green arrowhead, frt sequence. (B) Three polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers designed for detecting Ssbp1 exon 3. (C) Genotyping of Ssbp1+/+, Ssbp1+/−, and Ssbp1−/− tissues by indicated primers. (D) Morphology of Ssbp1+/+ and Ssbp1−/− embryos at E8.5. Scale bar, 0.5 mm. (E) Relative mtDNA levels in Ssbp1+/+, Ssbp1+/−, and Ssbp1−/− embryos assessed with real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR). Data are represented as means ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. (F) Survival curve of Ssbp1 conditional knockout mice (L/L, cre) and controls (L/L). (G) Heart-to-body weight ratio of L/L, cre and L/L. (H and I) Hematoxylin and eosin staining and COX/SDH staining of heart tissues from 17-week-old L/L, cre and L/L. Scale bars, 1 mm (H) and 100 μm (I).