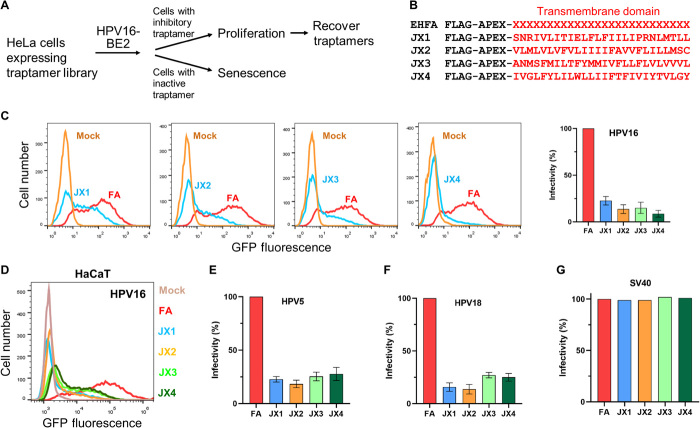
Fig. 1. Isolation of traptamers that inhibit HPV infection.
(A) Overview of scheme to isolate traptamers that inhibit HPV infection. See the main text for details. (B) Sequences of traptamers that inhibit HPV infection. In the EHFA library (top line), FLAG is the epitope tag, APEX is ascorbate peroxidase segment, and red “Xs” represent randomized hydrophobic positions. The red letters in other lines show the sequences of the hydrophobic segments of the four active traptamers in the single-letter amino acid representation. (C) Clonal HeLa-tTA cells stably expressing control FA (FLAG-APEX) (red) or JX1, JX2, JX3, or JX4 (blue) were infected at multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 2 with HPV16 PsV containing the green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter plasmid (HPV16-GFP). Two days later, GFP fluorescence was measured by flow cytometry to assess infectivity (histograms shown in left). Similar results were graphed in three independent cell lines for each traptamer, showing means and SD. (D) HaCaT-tTA cells expressing FA or the indicated traptamer were infected with HPV16-GFP PsV-GFP. Cells expressing FA were also mock-infected (brown). Two days later, GFP fluorescence was measured by flow cytometry and displayed as histograms. (E and F) Cells as in (C) were infected at MOI of 2 with HPV5-HcRed (E) or HPV18-HcRed (F) PsV. Two days later, HcRed fluorescence was measured by flow cytometry in three independent experiments for each PsV and graphed as in (C). (G) Traptamers do not inhibit SV40. HeLa-tTA cells expressing FA or the indicated traptamer were mock-infected or infected with SV40. Two days later, cells were stained with an antibody recognizing SV40 large T antigen and analyzed by flow cytometry. In all bar graphs, the results are graphed as % infectivity in cells expressing a traptamer normalized to cells expressing FA.