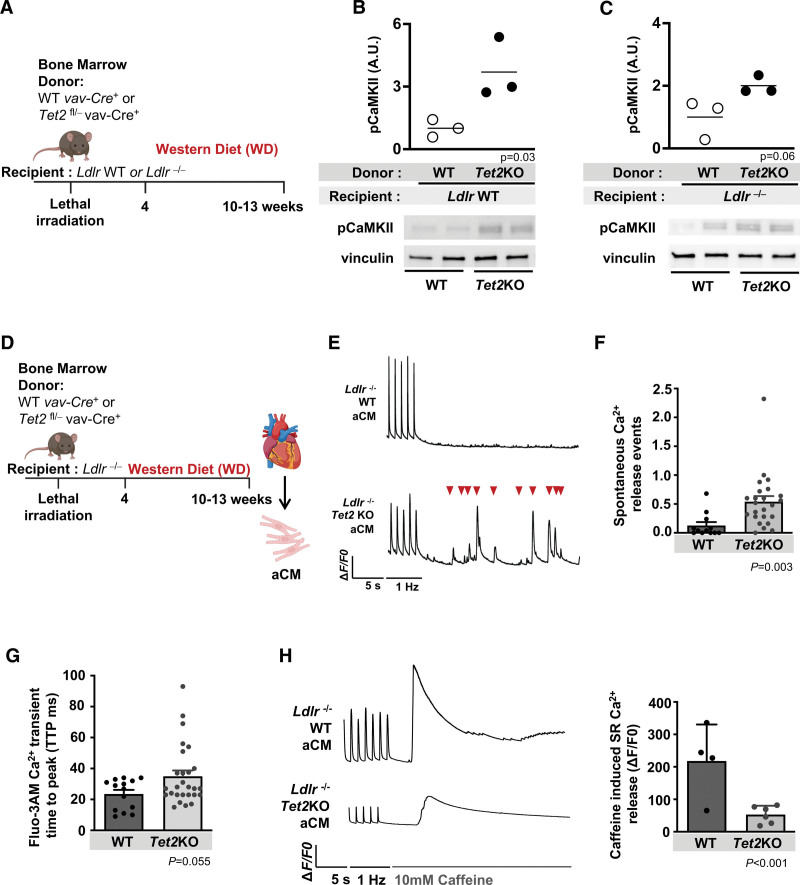
Figure 5.
Hematopoietic-specific inactivation of Tet2 leads to altered cardiomyocyte sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium release. A, Lethally irradiated Ldlr WT or Ldlr−/− mice were transplanted with bone marrow with hematopoietic-specific inactivation of Tet2 (Tet2KO) or WT controls and fed WD. B, Western blotting was performed to determine protein expression of phosphorylated calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) in atrial tissue of Ldlr WT and C, Ldlr−/− recipient mice. D, Lethally irradiated Ldlr−/− mice transplanted with bone marrow with hematopoietic-specific inactivation of Tet2 (Tet2KO) or WT controls were fed WD for 6 to 9 weeks. Atrial cardiomyocytes (aCM) were isolated and calcium studies performed using the calcium-sensitive dye Fluo-3 AM. E, Removal of pacing stimuli leads to spontaneous calcium release into cytosol (▼). F, Spontaneous calcium release events measured per second (data obtained from 2 mice per groups, n=12 events for WT and n=24 events for Tet2KO). G, Increased calcium transient amplitude measured during pacing (data obtained from 2 mice per groups, n=14 cells for WT and n=27 cells for Tet2KO). H, Removal of pacing stimuli and the addition of 10 mM caffeine leads to SR calcium emptying into the cytosol. Tracing to left, and quantification to right, showing reduced SR calcium release in Tet2KO aCMs (data obtained from 2 mice per group, n=4 cells for WT and n=6 cells for Tet2KO). △F/F0 is the change in fluorescence over baseline. Hz indicates the external pacing frequency stimuli. All Western blot quantification relative to loading control (vinculin) and then normalized. A.U., arbitrary units. Statistical tests: 2-tailed Student t test for all comparisons; linear mixed model for F through H. aCM indicates atrial cardiomyocte; KO, knockout; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; SR, sarcoplasmic reticulum; TET2, tet methylcystosine dioxygenase 2; WD, Western diet; and WT, wild-type.