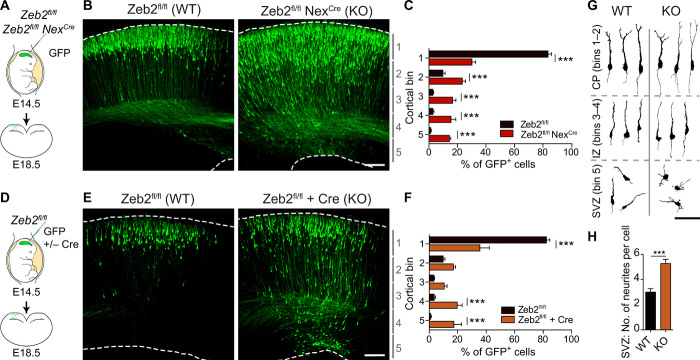
Fig. 1. Zeb2 promotes the onset of radial migration.
(A to C) Loss of Zeb2 causes laminar displacement of UL neurons. (A) Control (Zeb2fl/fl) and Zeb2-deficient (Zeb2fl/fl NexCre) littermate animals were in utero electroporated at E14.5 with a GFP expression construct and analyzed at E18.5. (B) Representative images of GFP+ neurons in neocortical slices. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) Laminar distribution of GFP+ cells in each cortical bin. The division of the neocortex into five equally sized bins is shown on the right. N = 12 Zeb2fl/fl and 5 Zeb2fl/fl NexCre animals. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni post hoc test. (D to F) Zeb2 regulates laminar position in a cell-intrinsic fashion. (D) Zeb2fl/fl animals were in utero electroporated at E14.5 with GFP in the presence or absence of Cre recombinase expressed under the postmitotic promoter Neurod1 (Cre) and analyzed at E18.5. (E) Representative images of GFP+ neurons in neocortical slices. Scale bar, 100 μm. (F) Laminar distribution of GFP+ neurons in vivo. N = 11 control and 6 Cre-expressing brains. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. (G) Morphology of GFP+ neurons in the CP, intermediate zone (IZ), or SVZ as indicated, at E18.5. Scale bar, 100 μm. (H) Number of neurites per cell for GFP+ neurons in the SVZ at E18.5. N = 15 per condition. Unpaired t test. KO, knockout; WT, wild type.