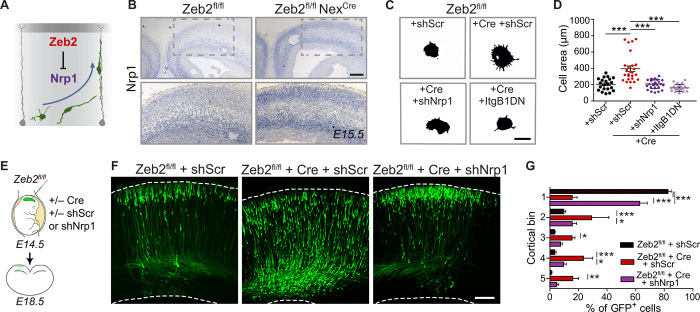
Fig. 4. Nrp1, a novel Zeb2-target, regulates the laminar position of UL neurons.
(A) Zeb2 represses Nrp1 expression. (B) ISH for Nrp1 in Zeb2fl/fl and Zeb2fl/fl NexCre animals at E15.5. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C and D) Nrp1 and integrins mediate enhanced adhesion of Zeb2-deficient neurons. (C) Adherence of Zeb2fl/fl primary cortical neurons transfected with scrambled short hairpin–mediated RNA (shScr), an Nrp1 shRNA (shNrp1) or ItgB1DN, and Cre as indicated to laminin-coated surfaces for 2 hours. Scale bar, 15 μm. (D) Lamellipodial spreading. N = 21 Zeb2fl/fl + shScr, 26 Zeb2fl/fl + Cre + shScr, 26 Zeb2fl/fl Cre + shNrp1, and 22 Zeb2fl/fl + Cre + ItgB1DN. One-way ANOVA (Kruskal-Wallis test) with Dunn’s multiple comparison test. (E to G) Zeb2 regulates laminar position through repression of Nrp1. (E) Zeb2fl/fl animals were in utero electroporated at E14.5 with shScr, shNrp1, and Cre as indicated and analyzed at E18.5. (F) GFP+ neurons in the neocortex. Scale bar, 100 μm. (G) Laminar distribution of GFP+ neurons at E18.5. N = 11 Zeb2fl/fl + shScr, 5 Zeb2fl/fl + shScr and Cre, and 7 Zeb2fl/fl + Cre + shNrp1 animals. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test.