Figure 4.
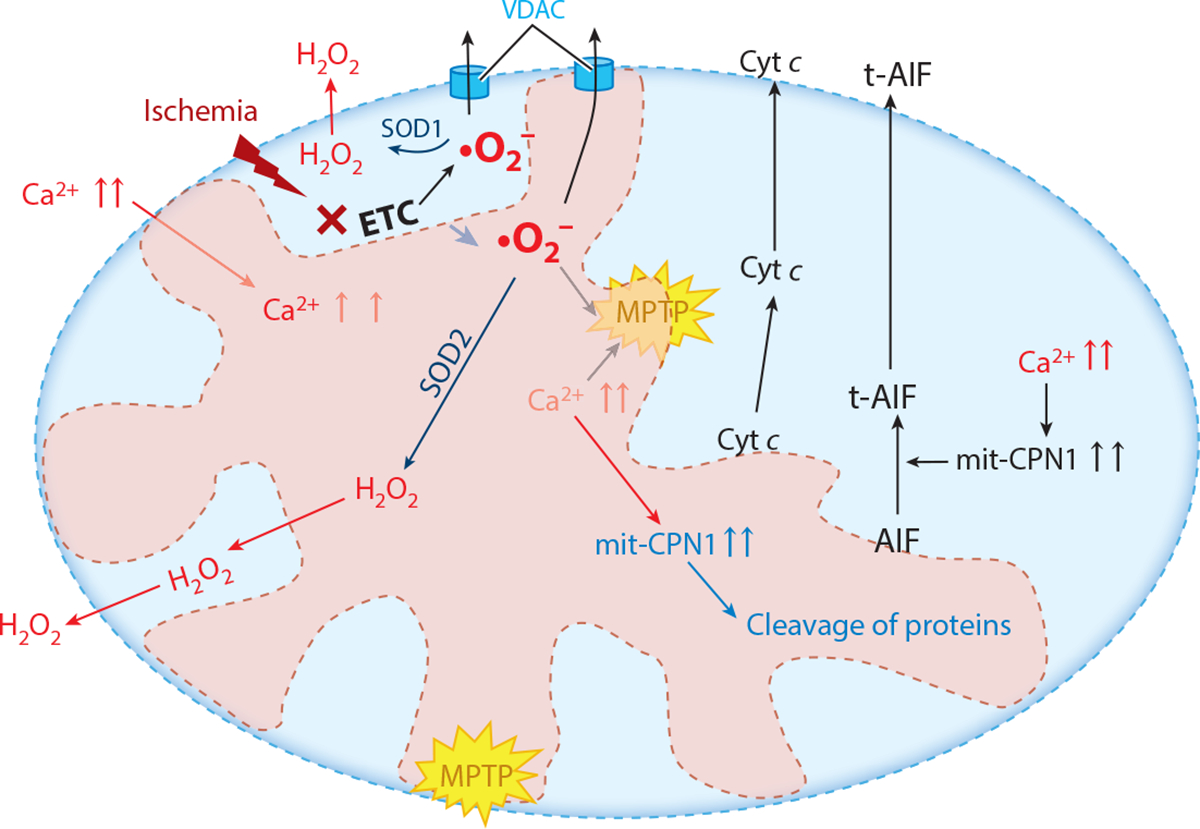
Mechanisms of mitochondrial-driven injury that result from ischemic damage to mitochondria, especially the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC). These include activation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) and permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane, leading to release of cytochrome c (Cyt c) and activation of mitochondrial calpains (mit-CPN1), which leads to the cleavage and release of truncated apoptosis-inducing factor (t-AIF) and the export of reactive oxygen species generated by the ETC by the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), including mitochondrial contact sites. Antioxidant systems include superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) in the mitochondrial matrix and superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) in the intermembrane space. Superoxide (•O2−) in the mitochondrial matrix is converted to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by SOD2, whereas superoxide in the intermembrane space is converted by SOD1 to H2O2.
