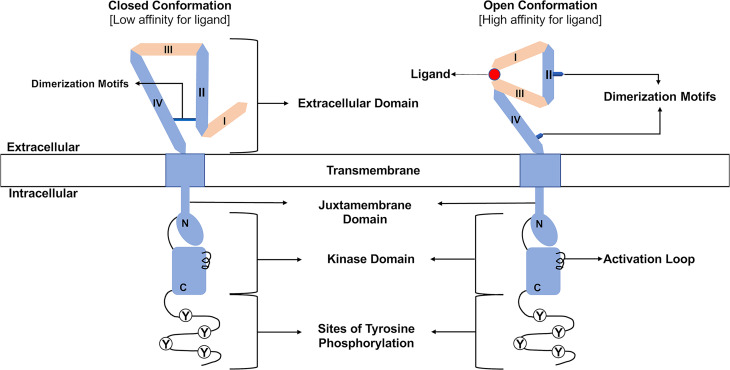
Fig. 1.
Organization of ERBB receptors. The amino-terminal extracellular region consists of four subdomains (I–IV) responsible for ligand binding and receptor dimerization. Note the dimerization motifs in subdomains II and IV that stabilize the intramolecular interactions characteristic of the closed conformation and enable the intermolecular interactions necessary for dimerization of two receptor molecules that exist in the open conformation. A hydrophobic transmembrane domain lies between the extracellular region and the cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. This kinase domain can be divided into amino-terminal (N) and carboxyl-terminal (C) lobes. Several sites of tyrosine phosphorylation (Y) reside at the carboxyl terminus of these receptors. Finally, note that ligand binding stabilizes a receptor molecule in the open conformation.