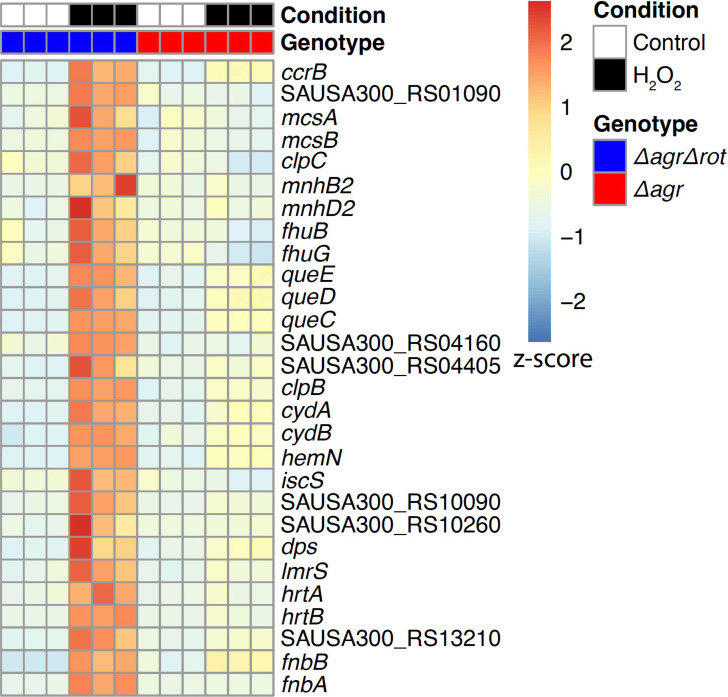
Figure 7. Rot-mediated up-regulation of H2O2-stimulated genes relative to those in an agr mutant.
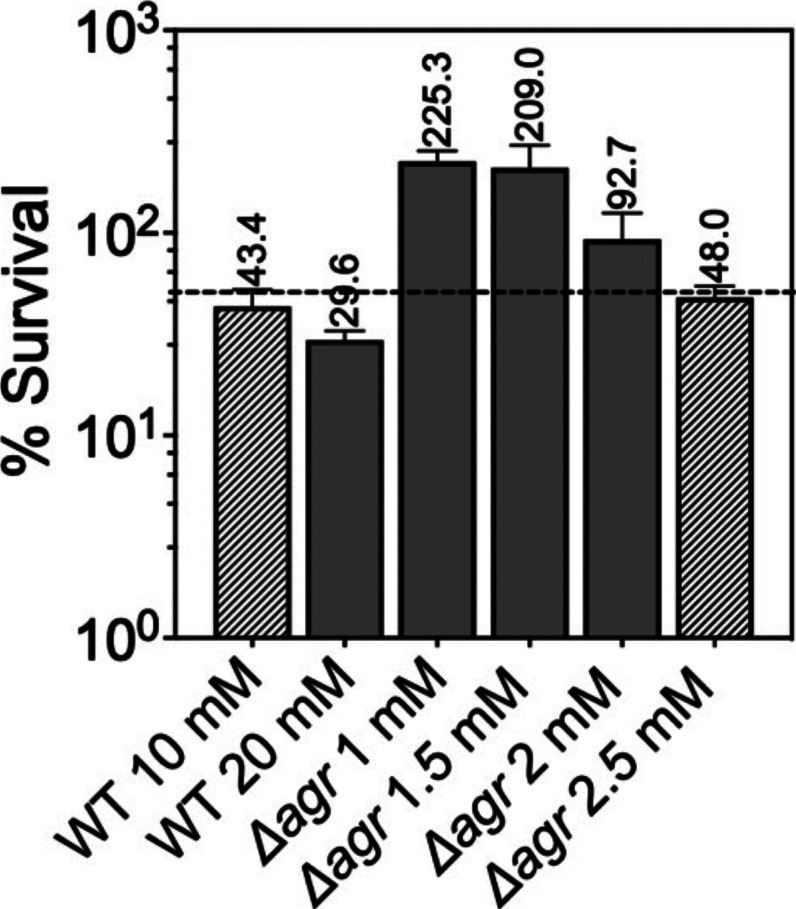
Genes shown are those up-regulated in a Δagr Δrot double mutant (BS1302) relative to that observed with the Δagr strain (BS1348). H2O2 treatment was for 30 min. Peroxide concentrations for Δagr (2.5 mM H2O2) and Δagr Δrot (10 mM H2O2) were determined to achieve ~50% cell survival [see Methods and Figure 7—figure supplement 1]. RNA-seq data are from three independent cultures. Heatmap colors indicate expression z-scores. See Supplementary file 3 for supporting information.