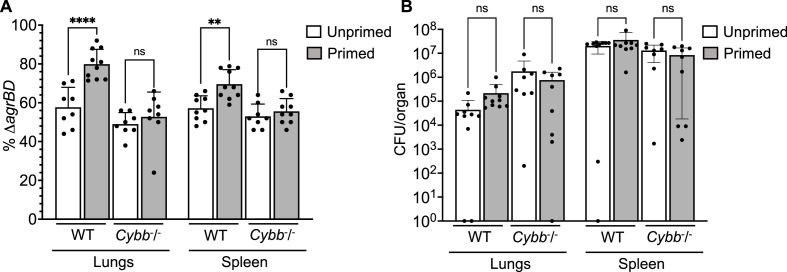
Figure 9. Survival advantage of agr priming of S.aureus absent in phagocyte NADPH-deficient murine infection.
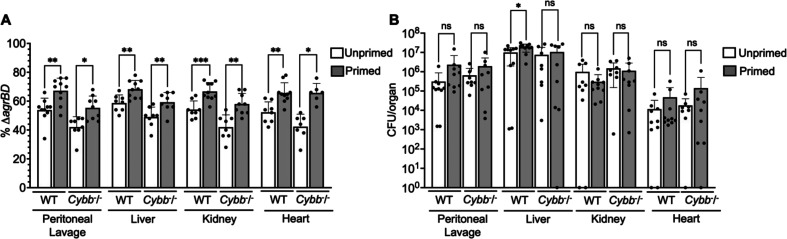
(A) percentage of ΔagrBD (AIP-responsive in-frame deletion mutant carrying an intact RNAIII) cells and (B) bacterial burden in lung or spleen after 2 hr of intraperitoneal infection of wild-type (WT) C57BL/6 mice or phagocyte NADPH oxidase-deficient (Cybb-/-) mice (see Figure 9—figure supplement 1 for data with other organs). ΔagrBD and ΔrnaIII mutant cultures were grown separately and mixed at a 1:1 ratio either before (primed) or after (unprimed) overnight growth, as for Figure 3. Both primed and unprimed mixtures were diluted after overnight growth, grown to early log phase (OD600∼0.15), and used as inocula (1 × 108 CFU) for intraperitoneal infection (n=2 groups of 10 mice each). After 2 hr, lungs and spleen were harvested and homogenized; aliquots were diluted and plated to enumerate viable bacteria. Output ratios and total and mutant colony forming units (CFU) from tissue homogenates were determined as for Figure 4E and H. A Mann-Whitney test (panel 9 A) or Student’s two-tailed t-test (panel 9B) were used to determine the statistical significance of the difference between primed and unprimed cultures. Error bars indicate standard deviation (**p<0.01; ****p<0.0001).