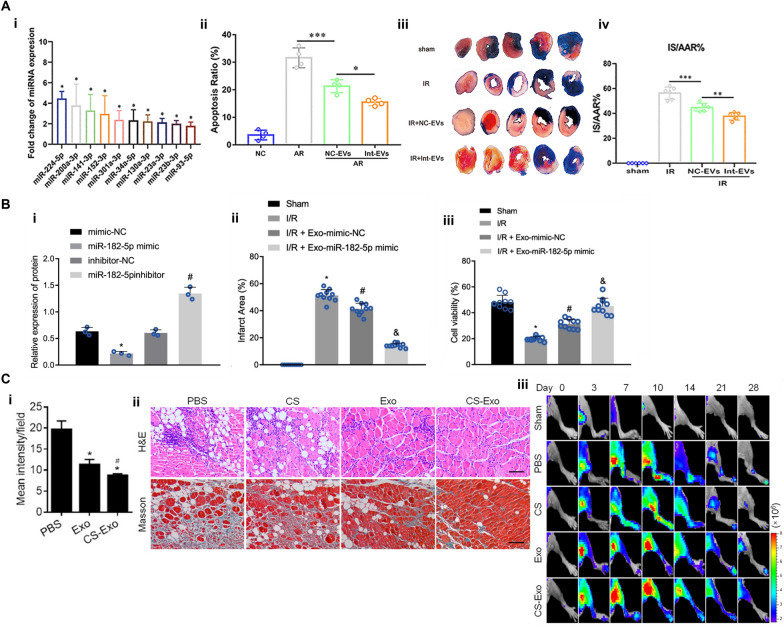
Fig. 3.
Exosome-based therapy for cardiac IRI. A Extracellular vesicles (EVs) produced by adipose-derived MSCs reduce pyroptosis and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes subjected to anoxia/reoxygenation (AR) by downregulation of pyroptosis related gene TXNIP. (i) Validation of differential EV-associated miRNA expression through qRT-PCR. (ii) Apoptosis detection in AR-exposed cardiomyocytes. The nC-EVs group was compared with the AR group and the Int-EVs group was compared with the nC-EVs group. (iii, iv) Assessment of infarct size (IS) and area at risk (AAR) in mice subjected to myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury [91]. B MSC-derived exosomal microRNA-182-5p alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting Gasdermin D (GSDMD) in mice. (i) Western blot analysis of GSDMD protein in myocardial cells, normalized to GAPDH. N = 10 for mice in each group. (ii) Myocardial infarction (MI) size diagram calculated by the cross-sectional imaging. (iii) The cell viability in myocardial tissues measured by Calcein-AM/PI double staining [93]. C Effects of MSC-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment. (i) Quantification of the apoptosis index of HUVECs administrated with exosome (Exo) and chitosan hydrogel to form hydrogel-incorporated Exo (CS-Exo) under H2O2-induced hypoxic stress. (ii) Representative images of muscle sections stained with H&E at day 14 and Masson’s trichrome at day 28 for apoptotic fibers analysis. Scale bar = 100 μm. (iii) In vivo monitoring of the status of angiogenesis following transplantation of CS-Exo or Exo through tracking Vegfr2-luc expression by bioluminescence imaging in mouse hindlimb ischemic models. Reprinted with permission from [101].
Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society