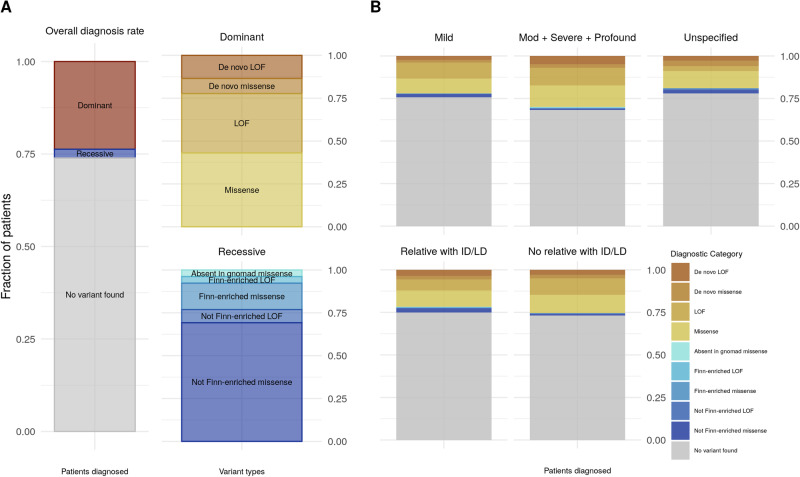
Fig. 4. Diagnostic rate in ID cases.
A Overall diagnostic rate for ID patients (25.62%, n = 281), of which 23.25% (n = 255) were found to have a heterozygous variant in a known dominant ID gene and 2.37% (n = 26) were found to have a homozygous variant in known recessive ID gene. B Diagnostic rate for patient subsets. The total diagnostic rate for moderate, severe, and profound ID (31.52%, n = 104) was higher than that of mild and unspecified ID (24.07%, n = 138). The total diagnostic rate for individuals without a family member with ID or a learning disability (26.7%, n = 160) was higher than that for individuals with a family member with ID/LD (24.31%, n = 121).