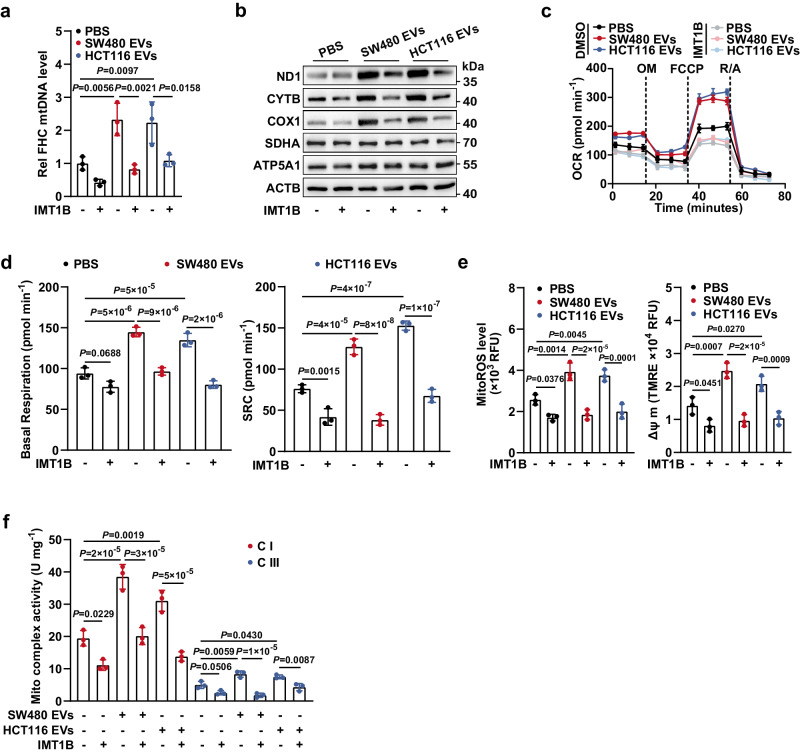
Fig. 3. EV-induced elevation of mtDNA content is responsible for the enhanced OXPHOS in CECs.
a FHC cells were educated with EVs derived from SW480 or HCT116 cells, in the presence or absence of IMT1B treatment (1 μM, 48 h). Then, the mtDNA content in FHC cells was determined. Rel, relative. n = 3 biological replicates. b Changes in expression levels of mtDNA-encoded proteins (ND1, CYTB, and COX1) and nuclear DNA-encoded mitochondrial proteins (SDHA and ATP5A1) in FHC cells. FHC cells were treated as described in a. The samples derive from the same experiment but different gels for SDHA, COX1, and ND1, another for ACTB, ATP5A1, and another for CYTB were processed in parallel. Changes in (c) OCR and (d) basal/spare respiratory capacities of FHC cells which were treated as described in a. SRC, spare respiratory capacity. n = 3 biological replicates. Changes in (e) mitochondrial ROS levels and ΔΨ m, and (f) activities of mitochondrial complex I and III in FHC cells. FHC cells were treated as described in a. n = 3 biological replicates. Data are means ± SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.