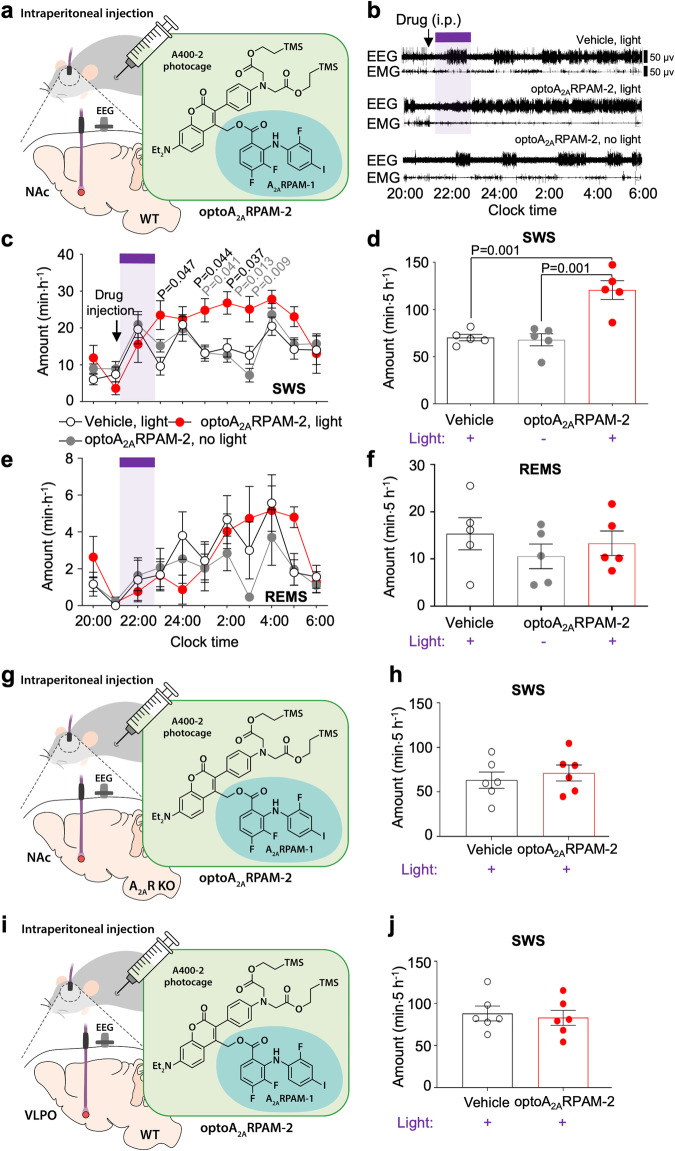
Fig. 6. Systemic administration of optoA2ARPAM-2 together with photoirradiation of the NAc in WT mice or A2AR KO mice and the VLPO in WT mice.
a Schematic diagram of systemic administration (intraperitoneal injection) of 150 mg kg-1 optoA2ARPAM-2 in WT mice and NAc photoirradiation with violet light (405 nm) for 1 h, illustrated by Sara Kobayashi. b Typical examples of EEG and EMG after administration of vehicle or optoA2ARPAM-2 in a WT mouse and NAc photoirradiation. Time course (c, e) and total amount (d, f) of SWS and REMS after optoallosteric NAc activation with optoA2ARPAM-2. Data (n = 5 biologically independent animals/group) are presented as mean ± SEM. Bonferroni t-test compared with vehicle (black font) or optoA2ARPAM-2/no light (gray font). c, e The purple bar indicates 1-h light illumination. Schematic diagrams of systemic administration (intraperitoneal injection) of 150 mg kg-1 optoA2ARPAM-2 in A2AR KO or WT mice and NAc (g) or VLPO (i), respectively, and photoirradiation with violet light (405 nm) for 1 h, illustrated by Sara Kobayashi. Total amount of SWS after optoallosteric NAc (h) or VLPO (j) activation with optoA2ARPAM-2. Data (n = 6 biologically independent animals/group) are presented as mean ± SEM. Source data have been deposited in the Figshare database [10.6084/m9.figshare.25468084]. Abbreviations: A2AR adenosine A2A receptor, EEG electroencephalogram, EMG electromyogram, i.p. intraperitoneal, KO knockout, NAc nucleus accumbens, REMS rapid eye movement sleep, SEM standard error of the mean, SWS slow-wave sleep, VLPO ventrolateral preoptic area, WT wild type.