Fig. 1.
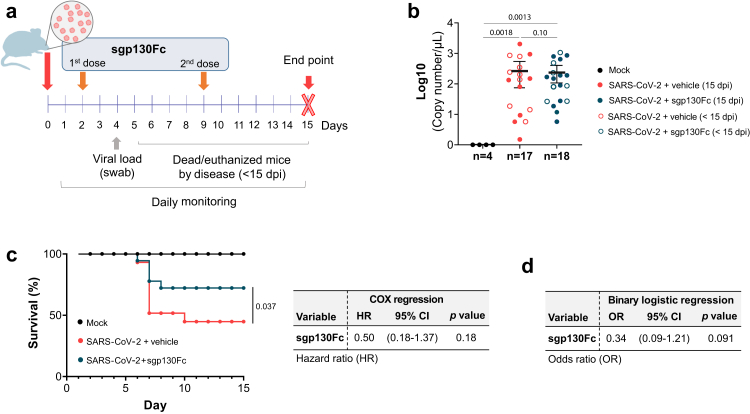
Experimental scheme and impact of IL-6 trans-signalling inhibition by sgp130Fc in SARS-CoV-2 infection-related mortality in K18-hACE2 mice. a) Experimental design for the animal study. Eight-month-old male K18-hACE2 mice were divided into three groups: i) mock (n = 4); ii) SARS-CoV-2 infected mice injected i.p. with vehicle (PBS) (n = 17); iii) SARS-CoV-2 infected and treated i.p. with sgp130Fc at 1 mg/kg per dose (n = 18). Mice were daily monitored until 15 dpi (experimental end-point). b) Viral load obtained from nasal swabs at four dpi quantified by qPCR. Sample size (n) of each group is indicated. Graph shows mean and 95% confidence intervals (CI) with each dot representing an individual animal. Statistics were calculated by Kruskal–Wallis test with Mann–Whitney U-test. c) Percentage of mice survival. COX regression analysis for sgp130Fc. HR: Hazard ratio. d) Univariate binary logistic regression analysis. p values were calculated as a function of Wald chi-squared. OR: odds ratio. Data are combined from two independent experiments. <15 dpi: dead/euthanized mice before the end of the experiment. 15 dpi: surviving mice at the end of experiment.