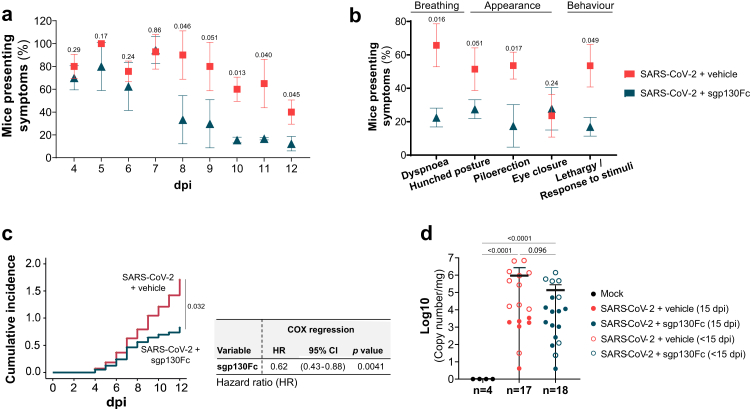
Fig. 2.
Effect of targeting lL-6 trans-signalling by sgp130Fc in symptomatology in SARS-CoV-2 infected mice. Analysed symptoms consisted on dyspnoea, hunched posture, piloerection and lethargy/staggering. a) Percentage of mice presenting at least one of the symptoms previously described. Daily significant differences between experimental groups were determined by Chi-squared test. b) Percentage of mice presenting individual symptoms considered as positive when a mouse showed it at any day during the period of follow-up. Significant differences between experimental groups were determined by Chi-squared test. c) Cumulative incidence of symptomatology during the follow-up timeframe and COX regression hazard model for sgp130Fc in the context of symptomatology development. HR: Hazard ratio. d) Viral load in lung tissue post-mortem (<15 dpi and 15 dpi) quantified by RT-qPCR. Graph shows mean and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Mock (n = 4); SARS-CoV-2 + vehicle (n = 17); SARS-CoV-2 + sgp130Fc (n = 18). Data are combined from two independent experiments. Statistics were calculated by Kruskal–Wallis test with Mann–Whitney U-test. dpi: days post infection. <15 dpi: dead/euthanized mice before the end of the experiment. 15 dpi: surviving mice at the end of experiment.