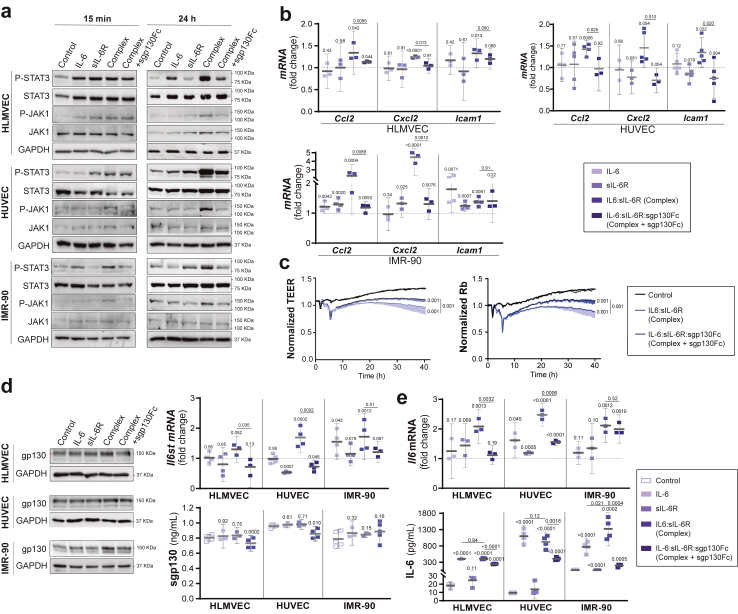
Fig. 7.
Effect of IL-6 trans-signalling on human endothelial cells and lung fibroblasts. Human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVEC), human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and human lung fibroblast (IMR-90) were treated with vehicle (control), IL-6 (20 ng/mL), IL-6R (20 ng/mL) or IL-6:sIL-6R (Complex, 20 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of sgp130Fc (300 ng/mL). a) Representative Western blot of P (Tyr705)-STAT3, STAT3, P (Tr1034/1035)-JAK1 and JAK1 from cell lysates after 15 min and 24 h of treatment. b) mRNA expression of proinflammatory markers (Ccl2, Cxcl2 and Icam1) by qPCR after 24 h of treatment. c) TEER assays performed in HLMVEC stimulated with vehicle (control) and IL-6:sIL-6R complex in the presence or absence of sgp130Fc. TEER was continuously measured for 40 h, and rabbit (Rb) was modelled with the ECIS software. d) Representative Western blots, Il6st (gp130) mRNA expression by qPCR and gp130 protein levels in supernatants from cultured cells after 24 h of treatment. e)Il6 mRNA expression by qPCR and IL-6 levels by ELISA in supernatants from cultured cells after 24 h of treatment. Data are combined from 4–3 independent experiments. Control is set to 1 for each experiment and data presented as fold-change vs control. Complex: IL-6:sIL-6R. Complex + sgp130Fc: IL-6:sIL-6R:sgp130Fc. All graphs show mean and 95% CI. Statistics were calculated by Kruskal Wallis test with Mann–Whitney U-test. p values vs vehicle-treated control (above) and vs complex (bar) are indicated in the graphs.