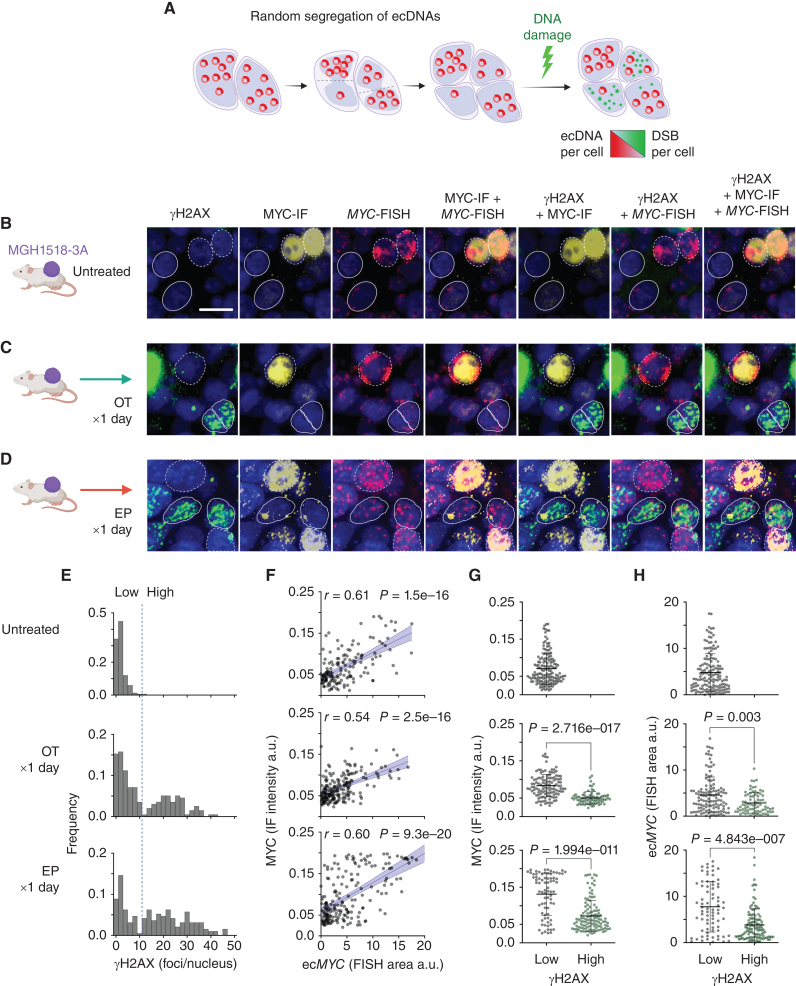
Figure 3.
ecMYC protects cells from DNA damage induced by chemotherapy. A, Schema to determine whether ecMYC protects cancer cells from DNA damage. Daughter cells inherit variable numbers of ecDNAs due to random segregation during mitosis. This generates natural copy-number heterogeneity that can be exploited experimentally to measure the effects of ecDNA dosage on therapy-induced DNA damage in individual tumor cells. B–D, MGH1518-3A xenografts (mean 58 copies ecMYC per cell) received either no treatment, a single day of OT, or a single day of EP and then were resected and fixed in formalin. Each xenograft tissue section was imaged by immunofluorescence for MYC protein and γH2AX, and by MYC-FISH for ecMYC content, with DAPI nuclear stain. γH2AX foci denote sites of DNA damage signaling, whereas homogenous γH2AX nuclear signals denote apoptotic nuclei. Dashed borders mark ecMYChigh cells, and solid borders mark ecMYClow cells. Scale bar = 10 μm. E, Distributions of γH2AX foci/nucleus. Treatment resulted in bimodal distributions with a clear threshold between damaged and undamaged cells (dashed line). F, Normalized MYC immunofluorescence vs. MYC-FISH area per nucleus. r = Pearson correlation coefficient, p = significance of correlation. G and H, MYC immunofluorescence (G) or MYC-FISH area (H) in nuclei with high or low γH2AX foci (with or without DNA damage), as measured by γH2AX foci/nucleus threshold in E. Created with BioRender.com.