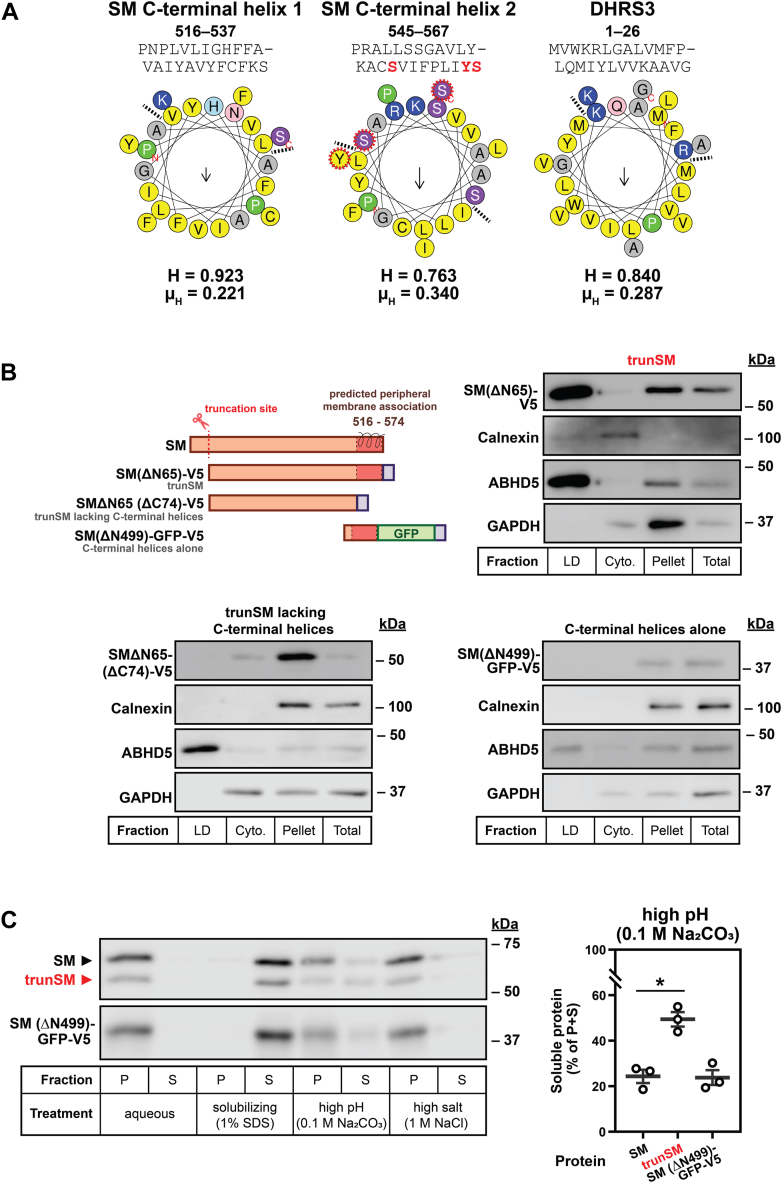
Figure 5.
The C-terminal helices of SM are necessary for lipid droplet association, but insufficient for peripheral membrane association.A, helical wheel projections of the two C-terminal helices of SM and the amphipathic helix required for lipid droplet localization of DHRS3 (13). Arrows indicate direction and magnitude of the hydrophobic moment (μH), which quantifies amphipathicity. Dotted lines indicate the border of the hydrophobic helix face. Known phosphorylation sites are indicated in red, and hydrophobicity (H) and μH scores are listed below each projection. Projections and scores generated using HeliQuest (81). B, HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated constructs for 24 h and treated with 450 μM oleic acid for 24 h. Lipid droplet (LD), cytosol (cyto.), pellet, and total fractions were collected, and levels of calnexin (endoplasmic reticulum marker), ABHD5 (LD marker), GAPDH (cytosol marker), and V5-tagged proteins of interest were determined by immunoblotting. See Fig. S4A for quantification. C, HEK293T cells were transfected with SM(ΔN499)-GFP-V5 for 24 h and refreshed in maintenance medium for a further 24 h. Membrane fractions were isolated and treated as indicated, followed by collection of pellet (P) and supernatant (S) fractions. Protein levels were determined by immunoblotting. Graph depicts the proportion of overall protein (P + S) found in the supernatant fraction. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 3 independent experiments (∗p ≤ 0.05; two-tailed ratio paired t test). ABHD5, abhydrolase domain-containing-5; DHRS3, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase-3; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; SM, squalene monooxygenase; trunSM, truncated SM.