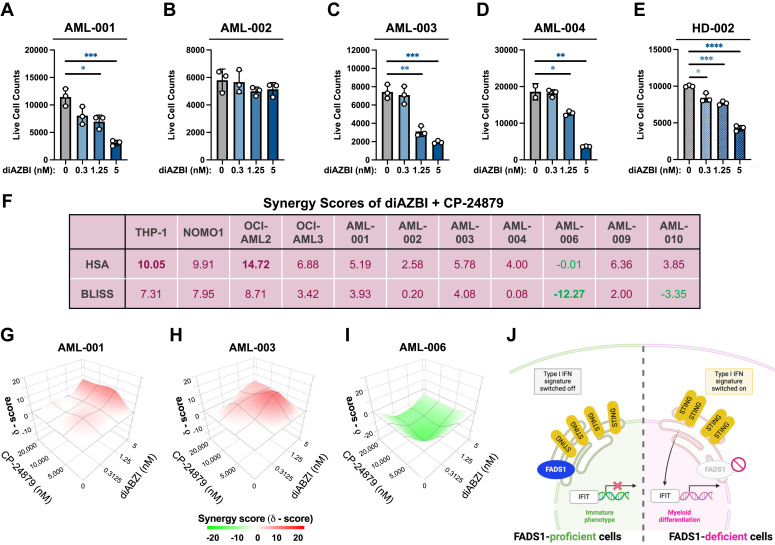
Figure 7.
STING agonism effectively eliminates patient-derived AML cells and variably cooperates with FADS1 inhibition.A–D, BM or PB samples recovered from patients diagnosed with AML were treated with the indicated concentrations of diAZBI for 4 days and then analyzed by flow cytometry to count live AML cells. A, AML-001: live cell counts, 0 versus 10 μM, ∗p = 0.0171 and 0 versus 20 μM, ∗∗∗p = 0.0009. B, AML-002: no significant differences. C, AML-003: live cell counts, 0 versus 10 μM, ∗∗p = 0.0014 and 0 versus 20 μM, ∗∗∗p = 0.0003. D, AML-004: live cell counts, 0 versus 10 μM, ∗p = 0.0189 and 0 versus 20 μM, ∗∗p = 0.0011. E, BM samples recovered from HD-002 were treated with the indicated concentrations of diAZBI for 4 days and then analyzed by flow cytometry to count live CD45+ cells. 0 nM versus 0.312 nM, ∗p = 0.0101; 0 nM versus 1.25 nM, ∗∗∗p = 0.0001; 0 nM versus 5 nM, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001). Dots represent individual data points and error bars represent SD. F, tabulation of the HSA (middle row) or BLISS (bottom row) synergy scores for the combination of diAZBI and CP-24879 assessed in the indicated cell lines or patient-derived AML samples. G–I, three dimensional plots of the synergy/cooperation scores (y-coordinate) for the indicated patient-derived AML samples treated with varying combinations of the STING agonist, diAZBI (z-coordinate), and CP-24879 (x-coordinate). J, a graphical summary of the molecular consequences of disrupting PUFA biosynthesis in AML. AML, acute myeloid leukemia; BM, bone marrow; FADS1, fatty acid desaturase 1; PB, peripheral blood; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid; STING, stimulator of interferon genes.