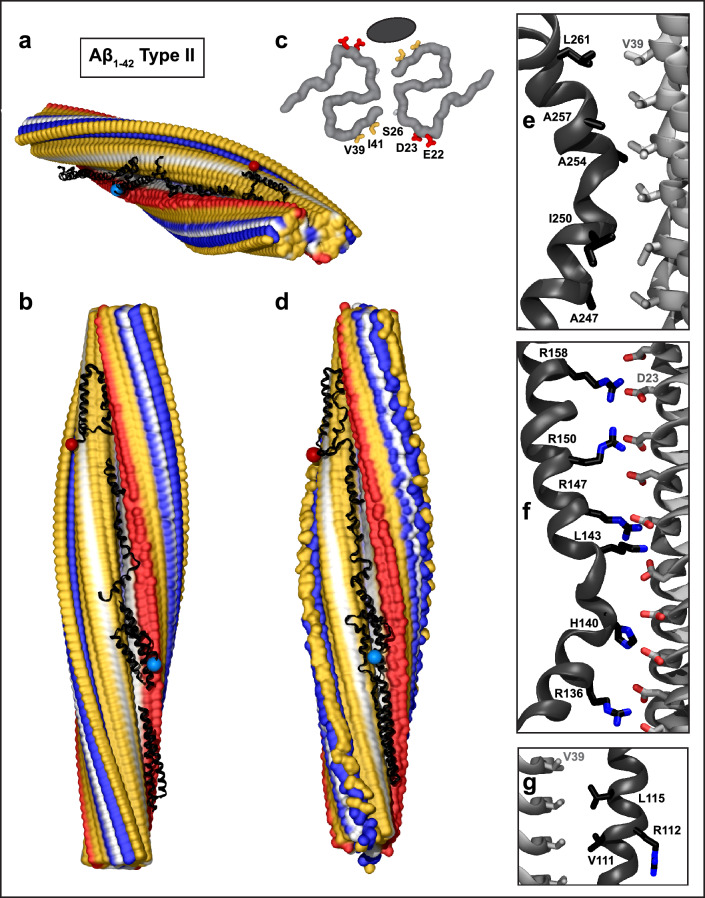
Fig. 2.
Structural model of full-length apoE in complex with Aβ1–42 type II fibril from AD vasculature. a, b Top and side views of the docking model, which was obtained using apoE segments shown in Supplemental Fig. 2d–h and the fibril structure (PDB ID: 7Q4M). Segment positions are compatible with full-length apoE. c Main chains of one fibril rung, top view. A black oval marks the apoE docking site at one of the two predicted symmetry-related sites per paired protofilament. ApoE-coordinating residues V39, I41 from molecule 1 and S26, D23, E22 from molecule 2 of the Aβ1–42 protofilament are shown. d The model of the full-length apoE in complex with the Aβ1–42 fibril after MD simulations. Panels e–g show apoE–amyloid contacts in selected regions of this model in a representative frame (apoE—black, Aβ—gray). e Hydrophobic interactions between CTD residues 247–261 of apoE and V39 ladder of Aβ1–42. f R158 in apoE3/E4 and other basic residues in helix 4 form favorable ionic interactions with the D23 ladder in Aβ1–42 amyloid. g Hydrophobic residues of apoE helix 3 interact with residue ladder V39 in Aβ1-42 amyloid. ApoE side chain 112 (R112 in apoE4) points away from amyloid