Fig. 6 |. Reduced immune investment in myeloid cells alters inflammatory and immunopathological responses of A. mexicanus.
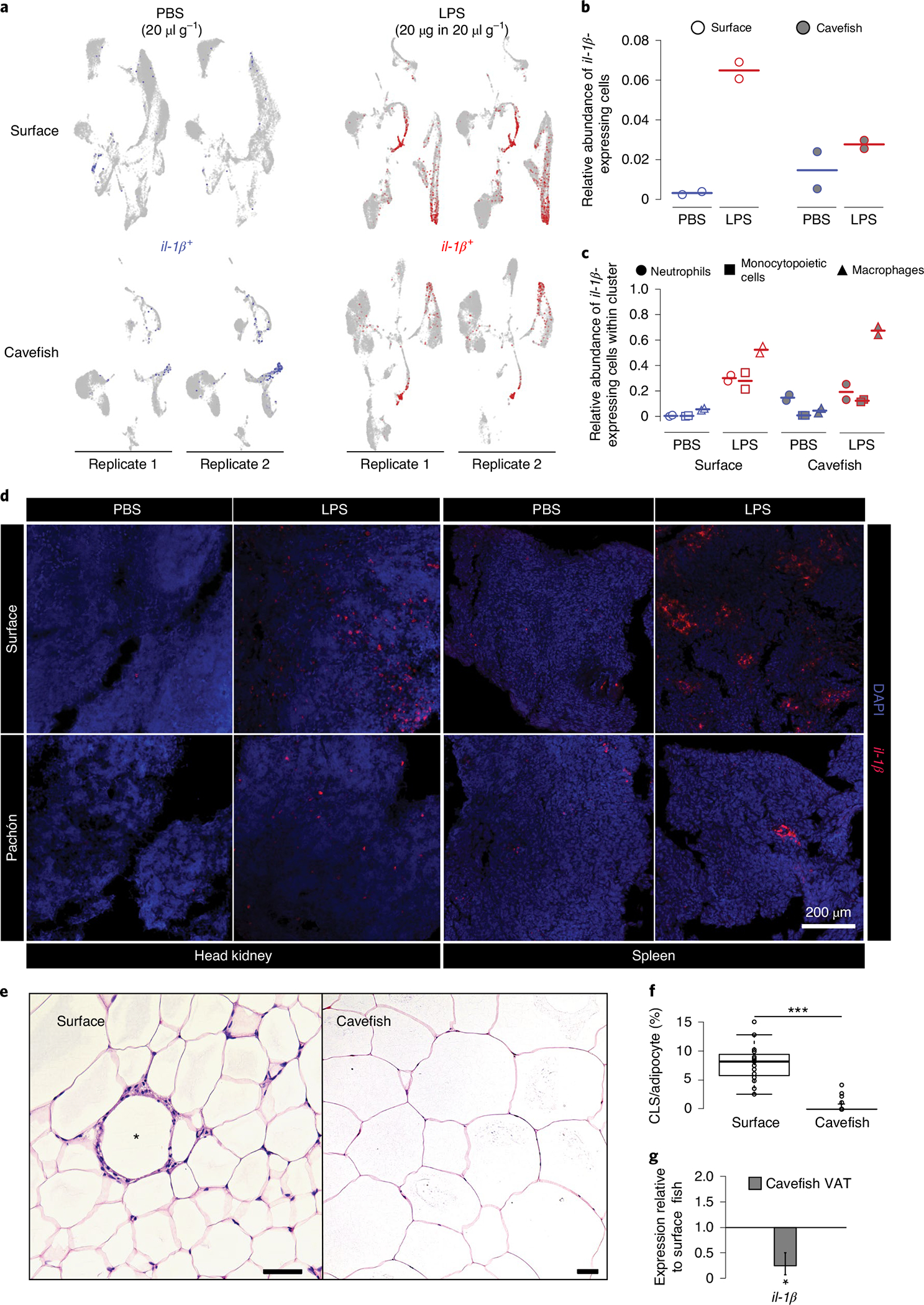
a, il-1β expression 3 h following PBS or LPS injection in HK cells. b, Overall relative abundances of il-1β-expressing cells from scRNA-seq experiments for each treatment group. c, Relative abundances of il-1β-expressing cells from scRNA-seq experiments within the main il-1β-expressing cell cluster for each treatment group. d, In vivo inflammatory response displayed by in situ hybridization of il-1β using RNA Scope in HK and spleen of surface fish and cavefish 3 h following intraperitoneal injection of 20 μg in 20 μl g−1 (bodyweight) LPS. Images are representative of two independent experiments. e, H&E staining of VAT of surface fish and cavefish. CLS is indicated by an asterisk in surface VAT. Scale bars, 50 μm. f, CLS count per 100 adipocytes in VAT of surface fish and cavefish in at least three fields of view for each fish (n = 3). Significance values were determined by Mann–Whitney U-test. For all box plots, centre lines show the medians, crosses show means, box limits indicate the 25th and 75th percentiles as determined by R software80, whiskers extend 1.5× interquartile range from the 25th and 75th percentiles and data points are represented by circles. ***P < 0.001. g, Gene expression of il-1β in cavefish VAT relative to surface fish (same fish that were used in f). Significance values were determined by a pairwise fixed reallocation randomization test using REST2009 software71; *P < 0.05. Error bar represents s.e.m.
