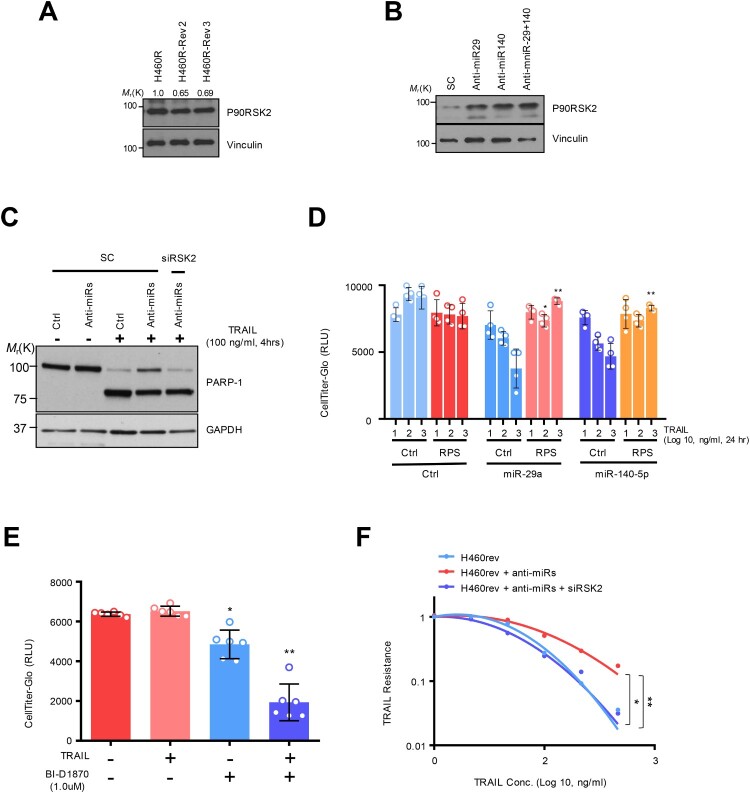
Figure 3.
RSK2 is responsible for H460 revertant phenotype. (A and B) Western blot analysis showing the alteration of RSK2 expression in H460R revertant cell. (C) Western blot analysis showing increased PARP-1 cleavage by targeting RSK2. H292 TRAIL-sensitive cells were treated with anti-miR-29 / -140 with siRSK2 siRNAs for 48h. Subsequently the cells were treated by TRAIL, followed by performing Western blot analysis as indicated antibodies. (D) Cell survival of the H460R cells in RSK2-dependent manner. The precursor of miR-29a or -140-5p was co-transfected with either empty vector or pcDNA-RPS6KA3 plasmid for 48h, and the cells were subsequently stimulated by TRAIL as indicated. After that, the CellTiter-Glo assay was performed to determine cell survival rate. P-value was calculated by two tailed student t-test (*p < 0.05, **p <0.01). (E) Enhanced TRAIL-sensitivity by pharmacologic inhibition of RSK2 activity. BI-D1870 was treated to H460R as indicated, and cell survival rate was determined by CellTiter-Glo assay. Bars shows mean ±SD (n = 6) and the p-values were calculated by two-tailed student t-test (* p < 0.01, **p < 0.001). (F) The re-sensitized TRAIL-sensitivity upon RSK2 suppression in cells harboring anti-miR-29 and -140-5p. Bars shows mean ±SD (n = 4) and the p-values were calculated by two-tailed student t test (*p < 0.01, **p < 0.001).