Figure 3.
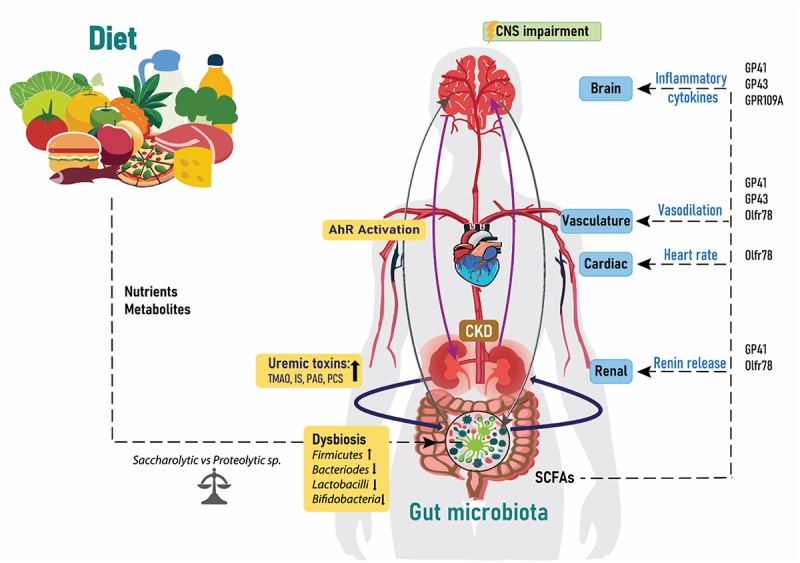
Diet, gut, brain and CKD. The relationship between the gut microbiota, kidney and brain is a circulatory process, which is influenced by the nutrients and metabolites from dietary choices. Increased bacterial changes lead to dysbiosis, which increases the release of uremic toxins into the circulation and activation of the AhR receptors and thereafter effects on the CNS. The amount of SCFAs from the gut microbiota influence renal renin release, heart rate and vasodilation and inflammatory cytokines through acting on the listed proteins. IS: Indoxyl sulfate; PCS: p-cresyl sulfate; TMAO: Trimethylamine N-oxide; PAG: Phenylacetylglutamine; CKD: chronic kidney disease; SCFAs: short chain fatty acids; CNS: central nervous system and AhR: aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
