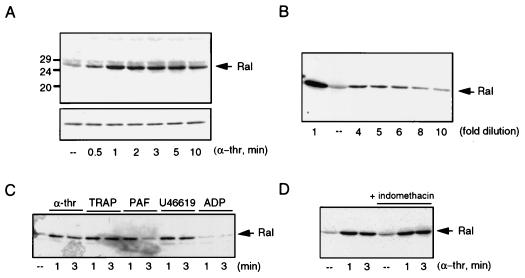
FIG. 2.
Stimulation of platelets with α-thrombin (α-thr) and other platelet agonists leads to rapid activation of Ral. (A) Activation of Ral by α-thrombin. Human platelets were isolated as described previously (18) and stimulated with 0.1 U of α-thrombin per ml for different times. The platelets were lysed and incubated with 15 μg of GST-RalBD precoupled to glutathione beads to recover GTP-bound Ral. Beads were washed four times, and collected Ral was identified by Western analysis with a monoclonal anti-RalA antibody (upper panel). The lower panel shows the levels of Ral in the whole lysates. (B) Determination of RalGTP induction. Platelets were stimulated with α-thrombin for 1 min and Ral activation was determined as described for panel A. In order to estimate the increase in RalGTP induced by α-thrombin, the α-thrombin-induced sample (far left) was diluted severalfold so it could be compared to the resting platelets (––). The gel shows that the signal obtained after a 6- to 10-fold dilution of the RalGTP obtained from α-thrombin-stimulated platelets matches the amount of Ral detected in resting platelets. (C) Ral activation by different platelet agonists. Platelets were stimulated for 1 and 3 min with 0.1 U of α-thrombin per ml, thrombin receptor-activating peptide (TRAP, 10 μM), PAF (200 nM), TxA2 analog U46619 (1 μM), or ADP (10 μM). Ral activation was analyzed as described for panel A. (D) Ral activation occurs independently of TxA2 formation. Platelets were treated with 30 μM indomethacin for 10 min to inhibit TxA2 formation, prior to stimulation with 0.1 U of α-thrombin per ml for the indicated times, or were stimulated with 0.1 U of α-thrombin per ml alone. At the concentration used, indomethacin inhibits TxA2 formation (not shown). Activation of Ral was monitored as described for panel A.