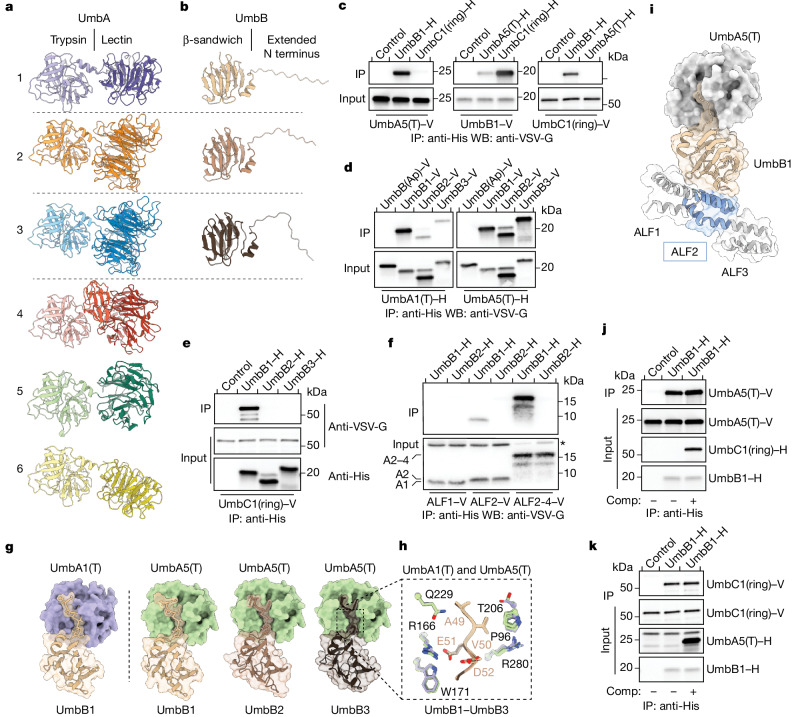
Fig. 2. PPIs in the Umb complex.
a,b Predicted structural models for UmbA1–UmbA6 (a) and UmbB1–UmbB3 (b) of S. coelicolor. Dashed lines separate pairs of proximally encoded proteins. c–f, Western blot (WB) analyses of IP experiments between the indicated heterologously expressed, tagged (hexahistidine (H) or VSV-G epitope (V)) Umb proteins. Control lanes correspond to beads in the absence of a bait protein. UmbB(Ap) is a UmbB protein from the distantly related species A. philippinensis. Bands corresponding to specific ALF repeats (ALF1 (A1), ALF2 (A2) and ALF2–ALF4 (A2–4)) and a background band (asterisk) are indicated in f. Additional input blots are provided in Extended Data Fig. 2. g,h, AlphaFold multimer-generated models for the interaction between the indicated UmbA and UmbB proteins of S. coelicolor, with surface representation highlighting the consistent predicted insertion of the N terminus of UmbB proteins into the major cleft of UmbA trypsin domains. Additional predicted N-terminal disordered residues of UmbB1–UmbB3 are removed for clarity. Inset in h depicts strictly conserved residues in UmbA and UmbB in proximity to the modelled interaction interface. Side chains coloured as in g, and numbering corresponds to positions in UmbA5 and UmbB3. i, Ternary complex combining AlphaFold multimer models of UmbB1–UmbA5(T) and UmbB1–ALF2 of UmbC1. Flanking ALF repeats in UmbC1 (grey) are shown for context. j,k, WB analyses of competitive binding experiments between UmbB1 and its partners UmbA5(T) and UmbC1(ring). Purified competitor (Comp) UmbC1(ring)–H (j) or UmbA5(T)–H (k) were added in excess to IP experiments involving UmbB1 and UmbA5(T) or UmbC1(ring), respectively. Uncropped blots are provided in Supplementary Fig. 1.