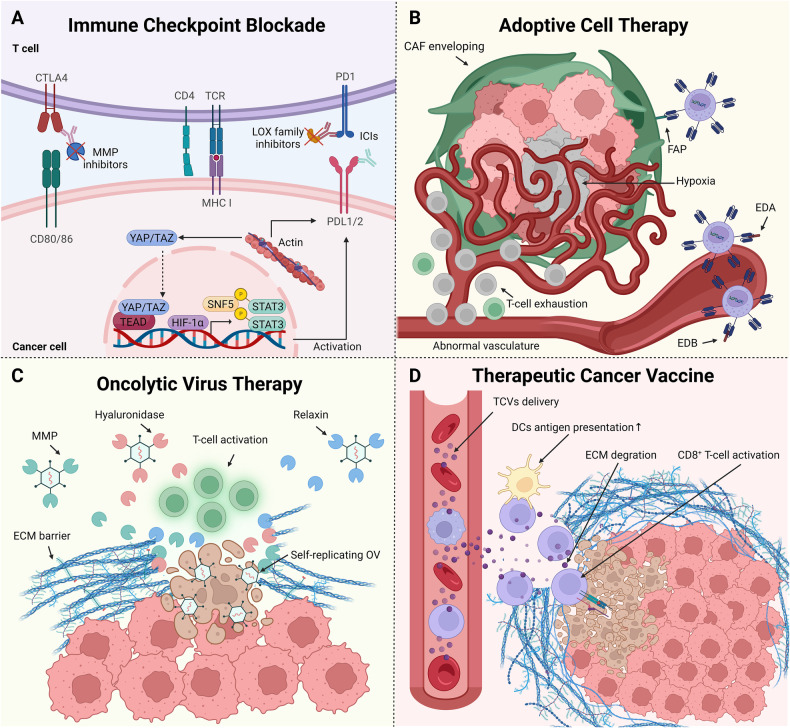
Fig. 5. Targeting ECM stiffness for improving the efficacy of immunotherapy.
A Mechanisms and strategies to counter high ECM stiffness in ICB. Elevated ECM stiffness modulates the expression of ICs through mechanotransduction signaling pathways. ICIs delivery is enhanced when combined with ECM remodeling agents like MMP and LOX inhibitors, enhancing ICB therapeutic efficacy. B Physical factors impeding CAR-T cell delivery and corresponding strategies. In tumors with high ECM stiffness, CAF encapsulation and abnormal vasculature obstruct CAR-T cell infiltration and lead to T-cell exhaustion. Targeting specific proteins, such as EDA, EDB, or CAF marker FAP, facilitates CAR-T cell penetration, effectively curtailing tumor growth. C Physical barriers to OV delivery and strategies to overcome them. The stiff ECM barrier hinders OVs from reaching tumor cells. Pairing OVs with ECM-degrading proteins, such as MMPs, hyaluronidase, or relaxin, breaks down this barrier, amplifying the OV’s cytotoxic effects by T-cell activation and self-replicating. D Therapeutic strategies for overcoming high ECM stiffness impeding TCV delivery. The stiff ECM barrier hampers TCV effects. TCVs combined with ECM-degrading agents promote antigen presentation of DCs and stimulates the activation of CD8+ T cell, thereby intensifying their cytotoxicity against cancer cells.