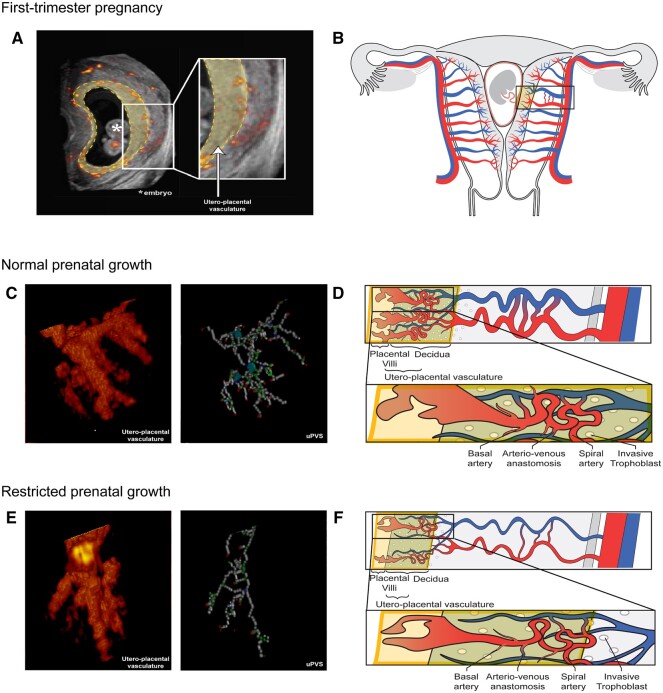
Figure 2.
Power Doppler ultrasound and schematic images of the utero-placental vasculature in a first-trimester pregnancy displaying normal and restricted prenatal growth. Overview of the utero-placental vasculature. (A) Two-dimensional (2D) power Doppler (PD) ultrasound image of a first-trimester pregnancy; all recorded vasculature is depicted in red-yellow colour. The yellow-highlighted section forms the virtual reality (VR)-based segmentation and corresponds with the yellow box in the schematic images. All vasculature in the VR-based segmentation is included in the utero-placental vascular skeleton (uPVS). (B) Schematic image of a first-trimester pregnant uterus including the uterine and placental vasculature (red, arterial vasculature; blue, venous vasculature). The yellow box contains decidua, invasive extravillous trophoblast and placental tissue which form the interface of the utero-placental vasculature. The vascular structures within the utero-placental vasculature are confined to the maternal basal and spiral arteries and their communicating arterio-venous anastomoses, and possibly vessels of the embryonic/foetal-placental blood space. (C) Enlarged section of a 3D PD ultrasound image of the utero-placental vasculature and uPVS in pregnancies with normal prenatal growth. The uPVS is characterized by an increased number of end- (red), bifurcation- (green), crossing- (blue), and vessel- (white) points when compared to pregnancies with restricted prenatal growth (as shown in panel E). (D) Schematic image of the utero-placental vasculature in pregnancies with normal prenatal growth, characterized by an increased absolute number of branches and arterio-venous anastomosis when compared to pregnancies with restricted prenatal growth. (E) Enlarged section of a 3D PD ultrasound image of the utero-placental vasculature and uPVS in pregnancies with restricted prenatal growth. The uPVS is characterized by a decreased number of end- (red), bifurcation- (green), crossing- (blue), and vessel- (white) points when compared to pregnancies with normal prenatal growth. (F) Schematic image of the utero-placental vasculature in pregnancies with restricted prenatal growth, characterized by a decreased absolute number of branches and arterio-venous anastomosis when compared to pregnancies with normal prenatal growth.